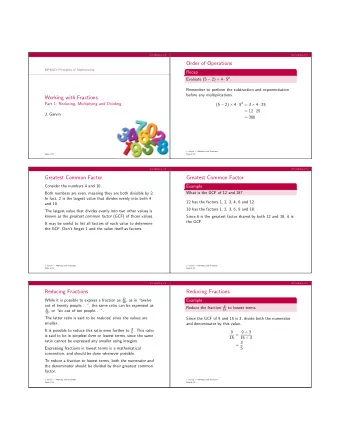
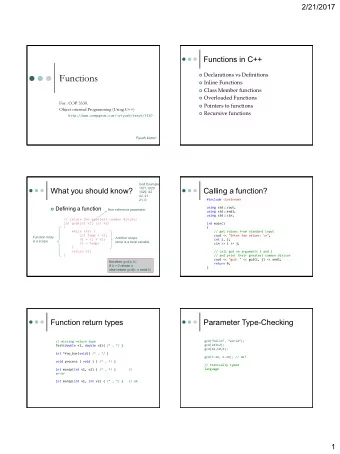
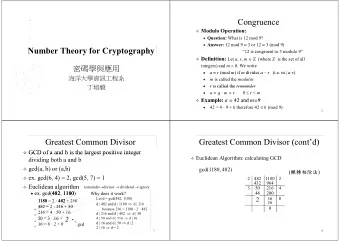
CSCI 3136 Principles of Programming Languages Summer 2013 Faculty - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
CSCI 3136 Principles of Programming Languages Summer 2013 Faculty of Computer Science Dalhousie University 1 / 62 Course Outline Introduction 2 / 62 Course Outline Introduction Programming language, History, Paradigms 3 / 62
CSCI 3136 Principles of Programming Languages Summer 2013 Faculty of Computer Science Dalhousie University 1 / 62
Course Outline • Introduction 2 / 62
Course Outline • Introduction • Programming language, History, Paradigms 3 / 62
Course Outline • Introduction • Programming language, History, Paradigms • Implementation 4 / 62
Course Outline • Introduction • Programming language, History, Paradigms • Implementation • Lexical analysis and automata theory • Syntactic Analysis and Context-Free Grammars • Semantic analysis • Names, scopes, and binding • Control flow • Data types and object-oriented programming • Specialized topics 5 / 62
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end.
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end.
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end.
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end.
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end.
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end.
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); Implementation end. 12 / 62
{ calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin Compiler/ read(i, j); Interpreter while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); Implementation end. 13 / 62
Compilation
Compilation Compiler
Compilation Source Program Compiler
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Target Program
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Input Target Program
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Input Target Program Output
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Input Target Program Output Interpretation
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Input Target Program Output Interpretation Interpreter
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Input Target Program Output Interpretation Source Program Interpreter
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Input Target Program Output Interpretation Source Program Interpreter Input
Compilation Source Program Compiler Target Program Input Target Program Output Interpretation Source Program Interpreter Output Input 26 / 62
Implementation Strategies: Example Virtual machine
Implementation Strategies: Example Virtual machine Source Program Intermediate Program Translator Intermediate Program Output Virtual Machine Input 28 / 62
Implementation Strategies: Example Linker
Implementation Strategies: Example Linker Incomplete Machine Source Program Compiler Language Machine Language Incomplete Machine Language Linker Program Library Routines 30 / 62
Implementation Strategies: Example The Preprocessor
Implementation Strategies: Example The Preprocessor Modified Source Pro- Source Program Preprocessor gram Modified Source Program Compiler Assembly Language 32 / 62
Implementation Strategies: Example Source-to-Source Translation (C++)
Implementation Strategies: Example Source-to-Source Translation (C++) Modified Source Source Program Preprocessor Program Modified Source Program C++ compiler C code C compiler Assembly Language C code 34 / 62
Phases of Compilation Character Stream Scanner (lexical analysis) Token Stream Parser (syntactic analysis) Parse Tree Symbol Table Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation Abstract Syntax Tree or Other Intermediate Form Machine-independent Code Improvement (Optional) Modified Intermediate Form Target Code Generation Target Language (e.g., assembly) Machine-specific Code Im- provement (Optional) Modified Target Language 35 / 62
Phases of Compilation Character Stream Scanner (lexical analysis) Token Stream Parser (syntactic analysis) Parse Tree Symbol Table Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation Abstract Syntax Tree or Other Intermediate Form Machine-independent Code Improvement (Optional) Modified Intermediate Form Target Code Generation Target Language (e.g., assembly) Machine-specific Code Im- provement (Optional) Modified Target Language 36 / 62
Phases of Compilation
Phases of Compilation Scanner (lexical analysis) Parser (syntactic analysis) Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation
Phases of Compilation Character Stream Scanner (lexical analysis) Parser (syntactic analysis) Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation
Phases of Compilation Character Stream Scanner (lexical analysis) Token Stream Parser (syntactic analysis) Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation
Phases of Compilation { calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end. Scanner (lexical analysis) Parser (syntactic analysis) Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation
Phases of Compilation { calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end. Scanner (lexical analysis) Parser (syntactic analysis) Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation
Phases of Compilation { calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end. Scanner (lexical analysis) { calculate greatest common divisor } Parser (syntactic analysis) program gcd ( input , output ) ; var i , j : integer ; begin read ( i , j ) ; while i <> Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i ; writeln ( i ) ; end .
Phases of Compilation { calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; - Remove comments begin read(i, j); while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end. Scanner (lexical analysis) { calculate greatest common divisor } Parser (syntactic analysis) program gcd ( input , output ) ; var i , j : integer ; begin read ( i , j ) ; while i <> Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i ; writeln ( i ) ; end .
Phases of Compilation { calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; - Remove comments begin - Remove extraneous read(i, j); characters while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end. Scanner (lexical analysis) { calculate greatest common divisor } Parser (syntactic analysis) program gcd ( input , output ) ; var i , j : integer ; begin read ( i , j ) ; while i <> Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i ; writeln ( i ) ; end .
Phases of Compilation { calculate greatest common divisor } program gcd(input, output); var i, j : integer; - Remove comments begin - Remove extraneous read(i, j); characters while i <> j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i; writeln(i); end. Scanner (lexical analysis) { calculate greatest common divisor } Parser (syntactic analysis) program gcd ( input , output ) ; var i , j : integer ; begin read ( i , j ) ; while i <> Semantic Analysis and Inter- mediate Code Generation j do if i > j then i := i - j else j := j - i ; writeln ( i ) ; end .
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.