COMP200 INTERFACES OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
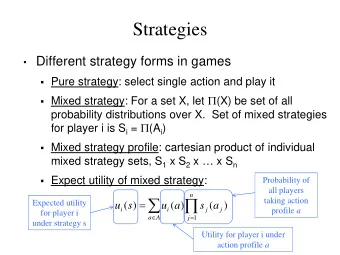
1 1 COMP200 INTERFACES OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 Interfaces 3 ANIMAL picture food sleep() roam() makeNoise() eat() 4 ANIMAL picture food sleep() roam() makeNoise() eat() CANINE FELINE roam() roam() 5
1 1 COMP200 INTERFACES OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed
2 Interfaces
3 ANIMAL picture food sleep() roam() makeNoise() eat()
4 ANIMAL picture food sleep() roam() makeNoise() eat() CANINE FELINE roam() roam()
5 ANIMAL picture food sleep() roam() makeNoise() eat() CANINE FELINE roam() roam() LION CAT WOLF DOG makeNoise() makeNoise() makeNoise() makeNoise() eat() eat() eat() eat()
6 Problem � Need to add Pet behaviors to the pet animal classes (Cat and Dog): • play()
7 Option 1 � Add concrete methods: Animal play() to Animal class Feline Canine Lion Cat Wolf Dog
8 Option 1 � Add concrete methods: Animal play() to Animal class Feline Canine � What’s the problem? Lion Cat Wolf Dog
9 Option 1 � Add concrete methods: Animal play() to Animal class Feline Canine � What’s the problem? Lion Cat Wolf Dog � Also exist for Lion/Wolf
10 Option 2 Add abstract methods: Animal play() to Animal class Feline Canine Lion Cat Wolf Dog
11 Option 2 Add abstract methods: Animal play() to Animal class Provide empty body for it Feline Canine in Lion and Wolf classes Lion Cat Wolf Dog
12 Option 2 Add abstract methods: Animal play() to Animal class Provide empty body for it Feline Canine in Lion and Wolf classes Provide non-empty body Lion Cat Wolf Dog for it in Cat and Dog classes
13 Option 3 � Add concrete methods: Animal play() to Cat and Dog classes Feline Canine Lion Cat Wolf Dog
14 What we need � Pet behaviors just in Pet classes (like Dog and Cat)
15 What we need � Pet behaviors just in Pet classes (like Dog and Cat) � Consistency - Guarantee that all Pet classes use the same signature for Pet methods
16 What we need � Pet behaviors just in Pet classes (like Dog and Cat) � Consistency - Guarantee that all Pet classes use the same signature for Pet methods � Take advantage of Polymorphism
17 Multiple Inheritance? Animal Pet Feline Canine Lion Cat Wolf Dog
18 Multiple Inheritance? Animal Pet Feline Canine Lion Cat Wolf Dog But Java does not allow multiple inheritance! Why?
19 Multiple Inheritance? � Not allowed � Mainly to avoid complexity/confusion. � Want to keep it simple.
20 The Diamond Problem SuperClass method() A B method() method() C
21 The Diamond Problem SuperClass method() A B method() method() C What happens when method() is called in C?
22 Solution: Interfaces Make Pet an interface and put all pet behaviors in it as abstract methods Animal Pet abstract play(); Feline Canine Lion Cat Wolf Dog
23 Interfaces � Classlike construct • contains only constants and abstract methods .
24 Interfaces � Classlike construct • contains only constants and abstract methods . • cannot contain variables or concrete methods.
25 Interfaces � Classlike construct • contains only constants and abstract methods . • cannot contain variables or concrete methods. � Declaration: public interface <InterfaceName> { // constant declarations; // method signatures; }
26 Interface Pet public interface Pet { public void play(); }
27 Implementing Pet interface class Dog extends Canine implements Pet{ public void play(){ System.out.println(“Catch ball”); } }
28 Implementing Pet interface class Dog extends Canine implements Pet{ public void play(){ System.out.println(“Catch ball”); } } class Cat extends Feline implements Pet { public void play(){ System.out.println(“Roll ball”); } }
29 Interface Characteristics � Interfaces are defined in their own file
30 Interface Characteristics � Interfaces are defined in their own file � Methods are abstract . No implementations. � May omit the abstract keyword.
31 Interface Characteristics � Interfaces are defined in their own file � Methods are abstract . No implementations. � May omit the abstract keyword. � Do not have instance fields .
32 Interface Characteristics � Interfaces are defined in their own file � Methods are abstract . No implementations. � May omit the abstract keyword. � Do not have instance fields . � Can have constant fields . Automatically treated as public, static, final; may omit any of these keywords
33 Example public interface Interface1 { int aNumber = 0; public void aMethod(); }
34 Example public interface Interface1 { int aNumber = 0; public void aMethod(); } Same as: public interface Interface1 { public static final int aNumber = 0; public abstract void aMethod(); }
35 Interface Characteristics � A class can implement any number of interfaces public class aClass implements I1, I2, I3 { // methods from I1, I2, I3... }
36 Interface Characteristics � A class can implement any number of interfaces public class aClass implements I1, I2, I3 { // methods from I1, I2, I3... } � Interfaces can not be instantiated
37 Interface Characteristics � A class can implement any number of interfaces public class aClass implements I1, I2, I3 { // methods from I1, I2, I3... } � Interfaces can not be instantiated � But can be used as a data type for a variable
38 Using the interface Pet[] pets = new Pet[2]; pet[0] = new Dog(); pet[1] = new Cat(); for(int i = 0; i < pets.length; i ++) pet[i].play();
39 Using the interface Pet[] pets = new Pet[2]; pet[0] = new Dog(); pet[1] = new Cat(); for(int i = 0; i < pets.length; i++) pet[i].play(); Similar to abstract classes – advantage of polymorphism
40 Classes from different inheritance hierarchy can implement same interface! Robot Animal Pet abstract play(); Feline Canine RoboDog Roomba Lion Cat Wolf Dog
41 Abstract Classes vs. Interfaces Variables Constructors Methods Abstract No restrictions Constructors are invoked by No restrictions. class subclasses through constructor chaining. An abstract class cannot be instantiated using the new operator. Interface All variables No constructors. All methods must be must be public public abstract static final An interface cannot be instantiated instance methods using the new operator.
42 Abstract Classes vs. Interfaces Variables Constructors Methods Abstract No restrictions Constructors are invoked by No restrictions. class subclasses through constructor chaining . An abstract class cannot be instantiated using the new operator. Interface All variables No constructors. All methods must be must be public public abstract static final An interface cannot be instantiated instance methods using the new operator.
43 Abstract Classes vs. Interfaces Variables Constructors Methods Abstract No restrictions Constructors are invoked by No restrictions. class subclasses through constructor chaining . An abstract class cannot be instantiated using the new operator. Interface All variables No constructors. All methods must be must be public public abstract static final An interface cannot be instantiated instance methods using the new operator.
44 Abstract Classes vs. Interfaces � Cannot inherit from multiple classes but, � Can can implement multiple interfaces � Interfaces = model “can-do” type relationships � Inheritance = model “is-a” type of relationship
45 Next Lecture � More on interfaces
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.