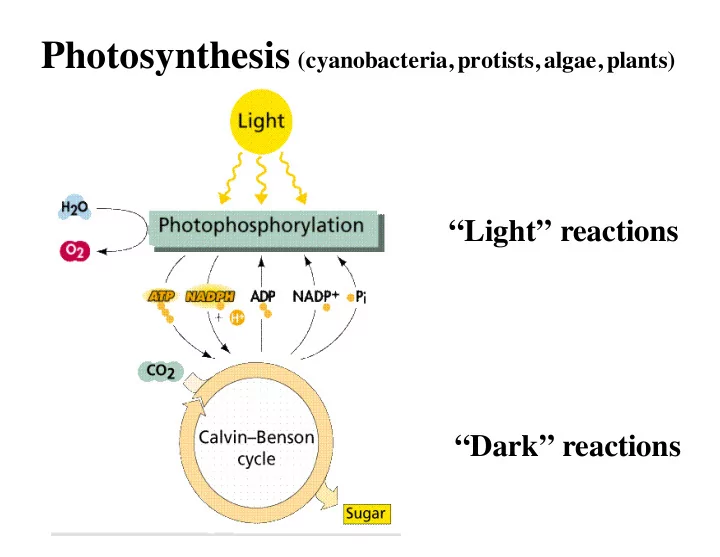

Photosynthesis (cyanobacteria, protists, algae, plants) “Light” reactions “Dark” reactions
light energy CO 2 + H 2 O Sugar + O 2
• 200 billion tons of CO 2 fixed per year • Different forms of carbohydrates produced (glucose, starch, cellulose, lignins…) • Basis of most food chains • Directly and indirectly supports animals
Herbivory: consumption of living plant tissues for food or water Similar to predation except: • generally does not kill the “prey” • “prey” generally cannot hide
• Grazer • Stem-borer • Leaf-miner
• Grazer • Stem-borer • Leaf-miner
• Grazer • Stem-borer • Leaf-miner
• Frugivore • Xylem-feeder • Phloem-feeder
• Frugivore • Xylem-feeder • Phloem-feeder
• Frugivore • Xylem-feeder • Phloem-feeder
Why Is The World Green? • Plants make lots of sugars • Plants are abundant • Plants cannot move
Chemical Defense Primary chemicals/metabolites : essential to plant growth and reproduction; found throughout plant kingdom (e.g. sugars, proteins, DNA, etc.) Secondary chemicals/metabolites : not essential to plant growth and reproduction; not universal throughout plant kingdom
“Quantitative” reduced digestibility (high conc.) lignins silica tannins “Qualitative” toxins (low concentration) alkaloids glucosinolates cyanogenic glycosides
Qualitative Alkaloids Numerous effects on metabolism & physiology… 14
Qualitative Glucosinolates Releases sulfur groups, found in Brassicaceae… 15
Qualitative Cyanogenic glycosides Releases HCN, cyanide blocks cellular respiration… 16
Milkweeds : sticky latex sap containing glycosides 17
18
Mechanical Defense • Prickles • Spines • Thorns • Waxy Cuticles • Trichomes 19
Urtica dioica (Stinging Nettle) Hollow, brittle hairs: 1. Histamine 2. Acetocholine 20
Constituent Defense: Defense mechanisms always operating in plant • many mechanical defenses • most quantitative chemical defenses Inducible Defense: Defense mechanisms that can be turned on by external cue • many morphological changes • many physiological changes • many qualitative chemical defenses 21
Ethnobotany: study of relationships between plants and people • Food (wild plants or agricultural) • Medicine • Fiber • Art • Spiritual
• Why are some plants delicious? • Why are some plants poisonous? • Why are some plants pokey? • What does “safe” mean?
• Poisonous • Side effects • Neutral • Beneficial
Poisonous: immediately Castor Bean White Snakeroot Deadly Nightshade / Beladonna
Poisonous: long term
Side Effects Opium Poppy Buckthorn Tobacco Coca
Neutral Grass Wood Cellulose Ponderosa Pine Kinnikinnick
Edible Plants of South Dakota • Sweeteners • Greens/Vegetables • Fruits • Flour • Flavoring/Tea
Factors Affecting Safety of Edible Plants
• Amount consumed
• Amount consumed • Details of preparation
• Amount consumed • Details of preparation • Part of plant consumed
• Amount consumed • Details of preparation • Part of plant consumed • Age or location of plant
• Amount consumed • Details of preparation • Part of plant consumed • Age or location of plant • Season of the year
• Amount consumed • Details of preparation • Part of plant consumed • Age or location of plant • Season of the year • Status of consuming person
Sometimes it’s hard to predict…
Sometimes it’s hard to predict… “Into the Wild”
39
Wild Potato aka Alpine Sweetvetch Hedysarum alpinum pp. 216-217 40
What killed Chris? • Theory 1: wrong plant (alkaloids) • Theory 2: Lathyrism (ODAP)
Lathyrism • Named after genus Lathyrus • Contains ODAP (protein) • Grass Pea sometimes consumed • Can cause leg paralysis • Young men more affected
What killed Chris? • Theory 1: wrong plant (alkaloids) • Theory 2: ODAP • Theory 3: another protein
What killed Chris? • Theory 1: wrong plant (alkaloids) • Theory 2: ODAP • Theory 3: another protein • Theory 4: normal starvation
Often there is contradictory info…
Safety????? Black Nightshade
Poisonous Plants of South Dakota
Sometimes bad (oxalates)…. Dock and Sorrel, Rumex pp. 304-305
Maybe bad (cardiac glycosides)… Milkweeds, Asclepias pp. 60-64 • Boil, don’t boil? • Change water, don’t change water? • Bitter, not bitter?
Bad (alkaloids)… Locoweed, pp. 222-224 • Swainsonine (from a fungus) • Most widespread problem poisonous plant in western North America • Loco disease or ‘pea struck’ • Chemotherapy • Native
Bad (alkaloids)… Monkshood aka Wolf’s Bane, pp. 310-311 • Aconitum • One of world’s most toxic plants • Digestive-cardiac-asphyxiation • Sometimes used for cardiac issues, nerve pain, cold feet —don’t use! • Native
Jimsonweed ( Datura stramonium ) (not in book)
Bad (alkaloids)… • Atropine & scopolamine • CNS & cardiac effects • Bad trips & death • Anesthesia & asthma treatment • Native to Mexico
Bad (alkaloids)… Poison Hemlock, pp. 48-49 • Coniine • CNS effects • Medicinal? • Non-native
Bad (alkaloids)… Water Hemlock, pp. 46-47 • Cicutoxin • CNS effects • Most poisonous plant in North America • Medicinal? • Native
Plant families to be super careful with… Plant families that are usually safe… 56
Recommend
More recommend