CHAPTER 11: MODEL TRANSFORMATION Transformation Definition - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Architecture and Modelling of Information Systems (D0I71A) Prof. dr. Monique Snoeck CHAPTER 11: MODEL TRANSFORMATION Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 2 Agenda Model Transformations General approach Transformation
Architecture and Modelling of Information Systems (D0I71A) Prof. dr. Monique Snoeck CHAPTER 11: MODEL TRANSFORMATION Transformation Definition Transformation Tool
2 Agenda Model Transformations General approach Transformation Rule Examples General Architecture The Enterprise Layer The Event Handling Layer Transformation Technology Example Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
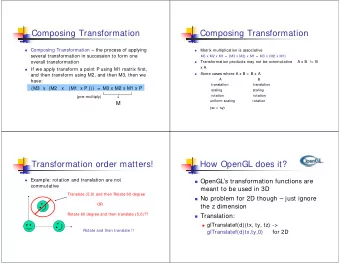
3 General Approach transformation engine models models or code transformation definition Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
4 General approach to transformations Develop software manually Look for patterns that are best practices Define Transformations based on patterns = Pushing patterns "below the water line" Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
5 Pushing Best Practices “below the line” DATABASE MGT SYSTEM (20xx) FLAT FILE (198x) Application Application Record insertion record insertion record deletion record deletion record search record search sorting sorting indexing indexing storage storage Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
6 Pushing Best Practices “below the line” Traditional MDA Specifications Specifications Object Other Interaction Object Architectural Pattern Other Interaction Pattern Architectural Pattern OO –relational Pattern Storage Pattern OO –relational Storage Pattern Code Code Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
7 Agenda Model Transformations General approach Transformation Rule Examples General Architecture The Enterprise Layer The Event Handling Layer Transformation Technology Example Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
8 General Transformation Architecture Business Process Business Process Engine Models User Interface Information Transactions System Services Queries Domain Event Handling Model Layer Enterprise Layer Persistence + Business Logic Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
9 Agenda Model Transformations General approach Transformation Rule Examples General Architecture The Enterprise Layer The Event Handling Layer Transformation Technology Example Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
10 The Enterprise Layer The Database Schema Domain Model Enterprise Layer Persistence + Business Logic Associations Navigability: one way or both ways ? Cardinality of ‘one’ transform to ‘many’ ? Optimisations Merge classes for ‘mandatory-one’ dependencies ? Transformation Definition Merge classes for ‘optional-one’ dependencies ? Transformation Tool 18:12
11 The Enterprise Layer The Database Schema = PSM for the EDG (=PIM) Class Project Foreign Key from Dependent to Master private Department owningDept Class Department Navigation from master to dependent too ? private SET(Project) projects Class Employee Transform cardinality of ‘one’ to ‘many ‘? private SET(DeptAssignment) assmtHistory Class Employee Transformation Merge Employee and DeptAssignment into Definition private Department mydepartement one database class ? Transformation Tool 18:12
12 The Enterprise Layer The Business Logic Domain Enterprise Layer Model Persistence + Business Logic Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
13 The Enterprise Layer (Business Logic) Business Logic Database Layer Abstract Class Object Type Implementation Class Factory 1 method per event type the object type participates in + 1 method for checking the corresponding preconditions Attribute of Attribute in Object Type Implementation Class Association Association Attribute Object Type Transformation in Implementation Class Definition participates in Transformation Tool 18:12
14 The Enterprise Layer (Business Logic) Business Logic Database Layer Abstract state class (associated with mapped class) Object Type's For each State of the FSM, a State subclass of FSM the mapped Abstract state class Per mapped State subclass, methods for checking state con- ditions for each event in of the mapped Abstract state class Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
15 The Enterprise Layer (Business Logic) Preconditions Code can be injected in different places In a check-event method in business layer or in the event handling layer Example: checking a precondition for a returnDate to be later than today Public boolean isValidReturnDate (Date d){ return d.compareTo(today) > 0 } … if isValidReturnDate(input_returnDate) { this .returnDate = input_returnDate; } else { throw new RuntimeException("return date is not valid.");} Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
16 Agenda Model Transformations General approach Transformation Rule Examples General Architecture The Enterprise Layer The Event Handling Layer Transformation Technology Example Domain Event Handling Model Layer Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
17 (Recap) A Business Event is ... A request to perform an activity to register something that happens or that you would like to happen in the real world. Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
18 (Recap)The Object Event Table identifies Business Event Types identifies Object Types models participation of Object Types to Business Event Types with an Object-Event-table (Decide on notification & coordination pattern later at implementation time) Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
19 (Recap)The Object Event Table In Merode, a business event is a request + an activity request can be refused When filled, a cell specifies what preconditions are imposed on a business event by a business object type Activity is distributed across participants (assuming that the request has been accepted) when filled, cell specifies what the effect is of that business event on the participating business object type (modified attributes, operation to call), Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
20 Transforming the OET to code OET-table ( PIM ) No immediate transformation to code ... Transform to UML- PSM Define collaboration diagram Transform Collaboration Diagram to code MERODE OET UML PSM/ Collaboration Code Diagram Messaging Pattern ? 1 pattern, applicable to all event types ! Transparent Maintenance easier Transformation tot non-OO platforms possible as well Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
21 Business Event Handling 1. Tasks Event Dispatcher Check Preconditions of all participants By Event Dispatcher By rule engine By Objects/Components Notify Event (broadcast) to participants Co-ordinate answers Check first – do then Do & compensate 2. How many Event Dispatchers ? Centralised versus Distributed one event handler for all events (maximally centralised) one event handler per event (maximally distributed) Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
22 Mapping Platform Independent Model Business Event Object Object/Event Involvement Mapping Platform Specific Model Mapping Rules for - Event Triggering - Precondition verification - Event Notification - Coordination of Event Execution Platform Choice - Programming Languages -EAI Middleware -Web Service Technology Transformation Definition -- ... Transformation Tool 18:12
23 Sample Event Handling Patterns Messaging Pattern should take care of: Event Notification to participants, precondition checking, Coordination of Event Execution Scheme 1: Forwarding 1 Not standardised ⇒ Must be designed for each event type separately More difficult to maintain E.g. take inspiration from OO-SSADM (UK) co-ordination of method invocation starts at home-entity Merode Forwarding can start in event owner Scheme 2: Broadcasting 2 one event handler per event (event class) (option chosen in code-generator) one event handler for all events of one type (C/M/E event dispatchers) (option chosen in JMermaid) Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
24 Event Forwarding In MERODE all receiving objects are connected with ED-relationship Initiate forwarding in Owner of Event Forward to Masters Questions How to ensure atomicity ? What if more than one Owner for an Event ? What with Event-preconditions ? (= preconditions for event in general, not for a method in a class) Transformation Definition Transformation Tool 18:12
25 Event Forwarding: example scheme General outline: PRODUCT TYPE Check first Do then (4) Checkmodify_quantity OK (4) modify_quantity Done PRODUCT ORDER OK (3) Check modify_quantity Done OK (3) modify_quantity (2) Check modify_quantity Done (2) modify_quantity ORDER LINE (1) Check modify_quantity Transformation Definition (1) modify_quantity Done Transformation Tool 18:12
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.