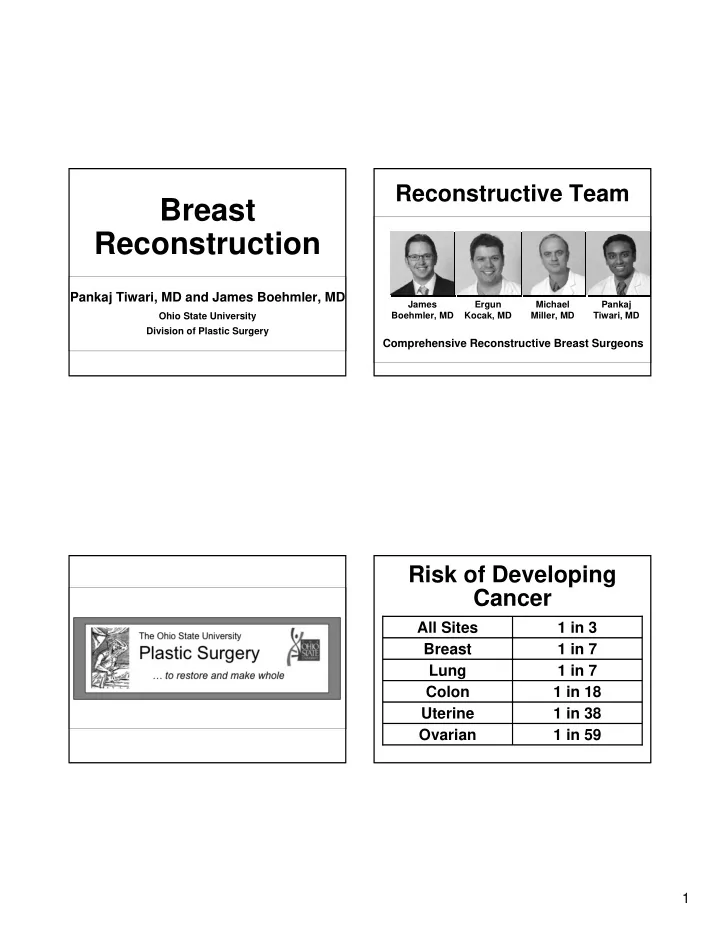

Reconstructive Team Breast Reconstruction Pankaj Tiwari, MD and James Boehmler, MD James Ergun Michael Pankaj Boehmler, MD Kocak, MD Miller, MD Tiwari, MD Ohio State University Division of Plastic Surgery Comprehensive Reconstructive Breast Surgeons Risk of Developing Cancer All Sites 1 in 3 Breast 1 in 7 Lung 1 in 7 Colon 1 in 18 Uterine 1 in 38 Ovarian 1 in 59 1
Mastectomy without Five Points to Remember About Breast Reconstruction Reconstruction 1) Elective • Advantages • Can always be performed later � No further surgery 2) Timing • � Shorter hospital stay Immediate vs. delayed 3) Symmetry � No additional risks • Journey, not a destination • Disadvantages 4) Revisions � Scar on chest wall • Frequently needed • www.breastform.com Smaller surgery � Asymmetry in clothing 5) Complications � External prosthesis • No surgery is risk-free • Uncomfortable • “Plan B” Reconstruction Options 1998 Federal Breast Reconstruction Law (1) Reconstruction of the breast on which the mastectomy has been performed None (2) Surgery and reconstruction of the other breast to produce a symmetrical appearance Immediate Timing (3) Prostheses and physical complications all stages of mastectomy, including lymphedemas Delayed Implants alone Tissue alone Technique Implants and tissue 2
Pschosocial Well-Being Aesthetic Outcome • Pronounced • Improved QOL asymmetry after BCS • Depression � Poor psychosocial fxn • Fear of recurrence, � Increased depressive • Stigmatization symptoms • Perceived change in � Stigmatization by health status. treatment Waljee et al. J Clin Oncol Referral Patterns Breast Conservation Therapy • Segmental • 24% gen surgeons mastectomy + XRT refer >75% patients • Survival data � Female surgeons • Increased local � High clinical breast recurrence volume, • Cosmetic Deformity � Work in cancer centers Alderman et al. Cancer. 2007 3
Skin Sparing Mastectomy Racial/Ethnic Disparity • Preserves Chest Skin • Reconstruction rate varies by race/ethnicity • Smaller Scar • 40.9% of whites, • Preferentially done • 33.5% of AAs, with Immediate Reconstruction • 41.2% of Latina-high • Not always possible � 13.5% of Latina-low � Previous Scars � Tumor Location www.breastcancer.org Alderman et al. Cancer. 2009 Skin Sparing Mastectomy Skin Sparing Mastectomy • Preserves Chest Skin • Preserves Chest Skin Smaller Scar Smaller Scar • • • Preferentially done • Preferentially done with Immediate with Immediate Reconstruction Reconstruction • Not always possible • Not always possible � Previous Scars � Previous Scars � Tumor Location � Tumor Location www.breastcancer.org www.breastcancer.org 4
Immediate Reconstruction Immediate Breast Reconstruction • Advantages � Lowers psychosocial morbidity � Lowers surgical morbidity � Better cosmetic results � Immediate breast mound present � No need for external prosthesis � No difference in detection of recurrence Immediate Tissue Expander with Silicone Implants Delayed Breast Reconstruction Immediate Breast Reconstruction � Advantages • Disadvantages � Mastectomy skin flap necrosis • Shorter hospital stay/ shorter recovery � More surgery, more pain • Chemotherapy and radiation therapy � Longer hospitalization/recovery causes no complications to reconstruction � Coordination required between surgeons • Allows patient time to consider options 5
Expander/Implant Delayed Breast Reconstruction • Most common reconstruction � Disadvantages • Usually multiple stages � Expander placement • Soft tissue scar on chest wall � Outpatient expansion � Expander/implant • Requires additional surgery and recovery exchange time • Single stage for smaller • Need for external prosthesis fr symmetry breast • Silicone vs. saline Selected Readings Plastic Surgery � Silicone - better feel � Saline - easier rupture detection Expanders and Implants Delayed Reconstruction www.mentorcorp.com 6
Tissue Expander Tissue Expander Patient Example Patient Example Implant Exchange Post-Operative Skin Sparing Mastectomy Mastopexy Appearance Expander/Implant Tissue Expander Patient Example Reconstruction • Advantages � Shorter surgery � Shorter hospital stay � Less technical surgery � Less pain? � Quicker recovery, return to work � Bilateral cases Placement of ADM along inframmary fold � Thin women 7
Expander/Implant Free Flap Breast Reconstruction Reconstruction � Different amount of “six pack” muscle taken � Full width of muscle • Disadvantages taken � Not permanent – Free TRAM � Implant material risks � Some muscle taken, some left behind • Capsular Contracture – Muscle sparing • Infection TRAM • Rupture � No muscle taken � Frequently need expansion – DIEP � Amount of muscle taken � Unilateral cases is dependant on patient’s � Radiation blood vessel anatomy Free Flap Breast CT Angiograms Reconstruction � Identifies blood vessels in the abdomen • Microsurgery � Microscope � Allows for more muscle preservation � Advanced training � Specialized centers • Abdomen most commmon • Other Sites � Buttock � Hip Selected Readings Plastic Surgery � Inner Thigh 8
Free Flap Free Flap Reconstruction Reconstruction Patient Example Patient Example Skin Sparing Mastectomy Free Flap Free Flap Breast Reconstruction Reconstruction • Advantages Patient Example � Permanent reconstruction � No implant material • No capsular contracture • No infections • No ruptures � “Tummy Tuck” � Skin sparing mastectomy � Physiologic � Long term cost savings 9
Secondary Surgeries Free Flap Breast Reconstruction • Disadvantages � Longer surgery � Longer hospitalization � Total failure risk <5% � More pain? � Not everyone a candidate • Too small • Too big • Previous abdominal surgeries Latissimus Dorsi Flap Other Surgeries • Pedicled flap reconstruction � Surgery to the other breast for symmetry • Usually combined with implant • Augmentation � “Mixed reconstruction” • Usually “Plan B” • Reduction • Benefits • Lift � No microsurgery � Nipple Reconstruction � Reliable � Fat Grafting • Risks � Tightness in back Selected Readings Plastic Surgery � Need implant 10
Recommend
More recommend