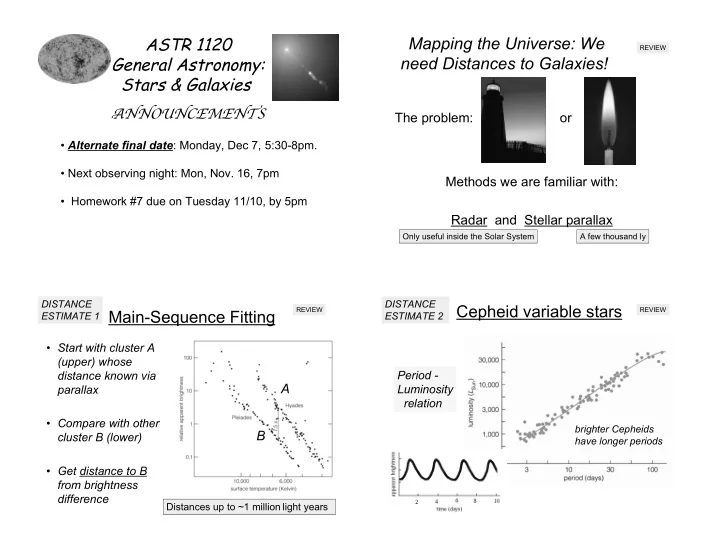

ASTR 1120 Mapping the Universe: We REVIEW General Astronomy: need Distances to Galaxies! Stars & Galaxies � NNOUNCEMENTS The problem: or • Alternate final date : Monday, Dec 7, 5:30-8pm. • Next observing night: Mon, Nov. 16, 7pm Methods we are familiar with: • Homework #7 due on Tuesday 11/10, by 5pm Radar and Stellar parallax Only useful inside the Solar System A few thousand ly DISTANCE DISTANCE Cepheid variable stars REVIEW REVIEW Main-Sequence Fitting ESTIMATE 1 ESTIMATE 2 • Start with cluster A (upper) whose distance known via Period - A Luminosity parallax relation • Compare with other brighter Cepheids B cluster B (lower) have longer periods • Get distance to B from brightness difference Distances up to ~1 million light years
Even brighter: DISTANCE DISTANCE Tully-Fisher Relation REVIEW REVIEW ESTIMATE 3 ESTIMATE 4 White dwarf supernovae • Nearly the same • Fast rotation speeds in amount of energy spiral galaxies released every � more mass in galaxy time. � higher luminosity why? Measure rotation speeds to infer luminosity • “Standard explosion” = fusion of 1.4 solar Need bright “edge-on” masses of spirals, estimate tilt material Distances up to ~1 billion ly Summary REVIEW Distance measurements allowed to “Distance Ladder” to measure universe make a MAJOR discovery about our Universe • Before 1924, “spiral nebulae” were thought to be small and located inside the Milky Way Different standard candles are useful for different distances
Hubble’s observations showed a very Andromeda found to be far outside Milky Way! startling result about the universe. • Edwin Hubble in 1924 identified Cepheids in • Vesto Slipher (1912) reported that most Andromeda (M33) � galaxies showed Doppler redshifts showed they were far • Edwin Hubble, using new 100” telescope, outside of Milky Way! started busily measuring galaxy redshifts – “Island Universes” • Hubble (1929) announced that redshifts of • His first big discovery! galaxies appear to increase with distance • But then he turned his attention to OTHER from us galaxies • This was startling: Suggested an Hubble using new EXPANDING UNIVERSE ! 100” Hooker telescope at Mt. Wilson (above LA) “Hubble’s Law” Hubble Space Telescope was v = H o � d designed to accurately measure Velocity of the Hubble constant Hubble’s Distance Recession Constant (Doppler Shift) (km/sec) (km/sec/Mpc) (Mpc) • High resolution velocity images to find faint Best current Cepheid variable values for stars in very distant expansion galaxies H o = 71+/- 4 distance km/s/Mpc
Clicker Question Clicker Question What is Hubble’s Law? What is Hubble’s Law? A. An idea stating that more distant galaxies move A. An idea stating that more distant galaxies move away from us faster than closer ones away from us faster than closer ones B. An equation giving the maximum luminosity for a B. An equation giving the maximum luminosity for a white dwarf supernova white dwarf supernova C. The relationship between the period and C. The relationship between the period and luminosity of a Cepheid variable star. luminosity of a Cepheid variable star. D. The law giving the maximum speed that a D. The law giving the maximum speed that a galaxy can move at. galaxy can move at. E. The idea that there are more galaxies outside E. The idea that there are more galaxies outside our own and that the universe contains immense our own and that the universe contains immense numbers of these “island universes.” numbers of these “island universes.” Balloon analogy for Clicker Question expanding universe What are the velocities of B, C and D • Each dot on the as measured by A? balloon can be thought of as a A. B: 1 cm/s; C: 2 cm/s; D: 3 cm/s galaxy. B. B: 3 cm/s; C: 1cm/s; D: 2 cm/s As the balloon expands, galaxies C. B: 2 cm/s; C: 4 cm/s; D: 6 cm/s move farther away from each other D. B: 1cm/s; C: 3 cm/s; D: 6 cm/s
Balloon analogy for Clicker Question expanding universe What are the velocities of B, C and D • On an expanding balloon, no galaxy is as measured by A? at the “center” of expansion; no edge A. B: 1 cm/s; C: 2 cm/s; D: 3 cm/s • Expansion happens B. B: 3 cm/s; C: 1cm/s; D: 2 cm/s into a higher dimension (2-D surface into a 3-D C. B: 2 cm/s; C: 4 cm/s; D: 6 cm/s space) D. B: 1cm/s; C: 3 cm/s; D: 6 cm/s • Is our 3-D space expanding through a 4 th dimension? Clicker Question A Better Way To Image the Expanding Universe No matter which direction we look, we see • NOT like an explosion of galaxies galaxies moving away from us. Therefore, we THROUGH space from a center place must be at the center of the expansion. A. True • The space BETWEEN galaxies is expanding, carrying the galaxies away B. False from each other – Why don’t galaxies themselves expand? Gravity!
Clicker Question The Cosmological Principle The universe looks about the same no No matter which direction we look, we see matter where you are within it galaxies moving away from us. Therefore, we must be at the center of the expansion. • Matter is evenly distributed on very large A. True scales in the universe B. False • No center & no edges • Not proven but consistent with all observations to date Since the universe “Hubble’s Law” is expanding, light traveling through the v = H o � d universe “feels” the stretch as it travels Velocity of Hubble’s Distance Recession Constant (Mpc) (Doppler Shift) (km/sec/Mpc) (km/sec) velocity Implies the Expansion of the Universe! distance Cosmological Redshift
Clicker Question Clicker Question What does the “expansion of What does the “expansion of the universe” most accurately the universe” most accurately mean? mean? A. Galaxies are moving apart through space A. Galaxies are moving apart through space B. Space itself is expanding B. Space itself is expanding C. Everything is expanding, including the earth, C. Everything is expanding, including the earth, our bodies, etc our bodies, etc D. The Milky Way is at the center of the D. The Milky Way is at the center of the universe and all other galaxies are universe and all other galaxies are expanding away from us. expanding away from us. Clicker Question Clicker Question Your friend leaves your house. She later calls you on her Your friend leaves your house. She later calls you on her cell phone, saying that she’s been driving at 60 mph cell phone, saying that she’s been driving at 60 mph (miles per hour) directly away from you the whole time (miles per hour) directly away from you the whole time and is now 60 miles away. Without looking at your and is now 60 miles away. Without looking at your watch, can you tell how long has she been gone? watch, can you tell how long has she been gone? A. Yes, 1 minute A. Yes, 1 minute B. Yes, 30 minutes B. Yes, 30 minutes C. Yes, 60 minutes C. Yes, 60 minutes D. Yes, 120 minutes D. Yes, 120 minutes E. No, not enough information to tell E. No, not enough information to tell
Expansion and the Age of the Is this anywhere near correct? Universe IF the universe has been expanding at the same speed • Age of the solar system ~ 4.6 billion years always: Distance = velocity � time � time = distance/velocity Hubble’s Law: v = H o � D � H o = velocity/distance • Age of the oldest star clusters ~ 13 billion Time (Age) = 1 / H o years For 71 km/sec/Mpc: Age ~ 13.7 billion years • General agreement, but we’ll revisit the assumption of constant expansion soon.. For larger H o , shorter time For smaller H o , longer time
Recommend
More recommend