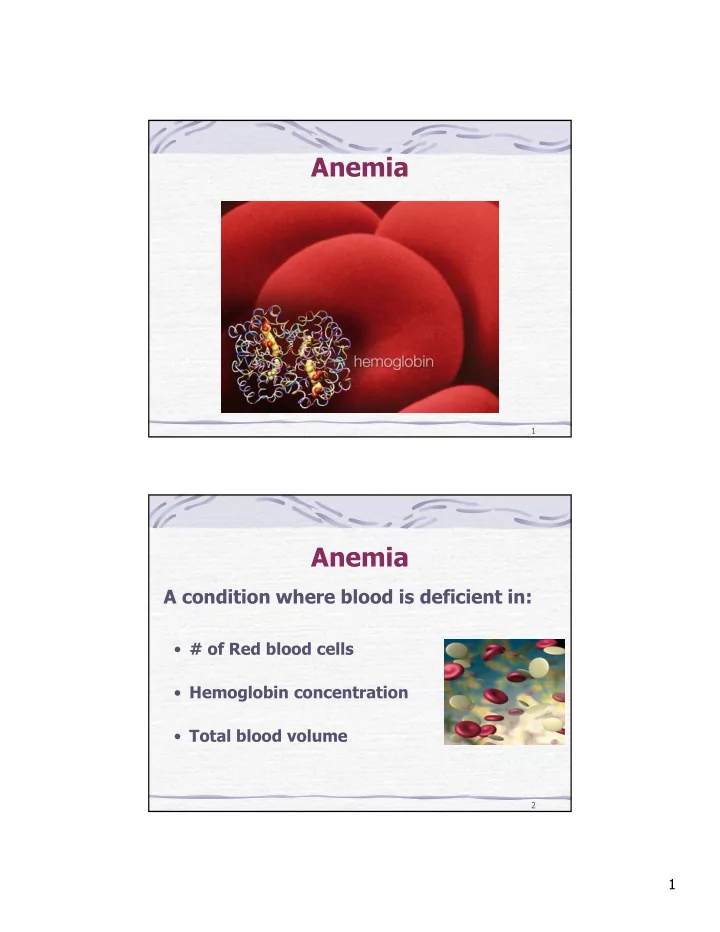

Anemia 1 Anemia A condition where blood is deficient in: • # of Red blood cells • Hemoglobin concentration • Total blood volume 2 1
Anemia Definition Hemoglobin [Hgb] concentration is 2 {std} deviations below the mean [Hgb] for a normal population for the same gender and age range. 3 Hemoglobin (Hgb) Function • Transports O2 from the lungs to the tissues • Transports CO2 back to the lungs & exhaled 4 2
Hemoglobin (Hgb) • Influenced by age, sex, altitude, & smoking • Normal ranges: New born babies: 17- 22 gm/dL Children: 11-13 gm/dL Adult women: 12-16 gm/dL 5 Causes of Anemia • Blood cell loss from the body - surgery, hemorrhage, Menstruation • Decreased lifespan of the red blood cell - Hemolytic anemia i.e., sickle cell anemia • Growth spurts • Pregnancy: - Inability of mom to keep up with red blood cell production for the growing fetus (should get 30mg of iron per day.) 6 3
Other Causes of Anemia • Chronic illness or infection can cause the body to make fewer red blood cells • Some drugs & medical treatments • Aplastic anemia: the inability for bone marrow to produce enough RBC (could be side effect of chemo, etc.) • Renal Disease, cancer 7 Most Common Cause of Anemia Iron Deficiency 8 4
Populations at Risk for IronDeficiency • Infants: not receiving adequate iron in their diet • Children: rapid growth spurts where iron available cannot keep up with RBC production • Women: blood loss during menstruation • Pregnant women: growing fetus has a high demand for iron 9 Infants at Risk for IronDeficiency • Not receiving adequate iron in their diet (watered down formula) • Infants at 6 months require dietary iron (iron stores have become depleted from birth) • Premature infants may require supplementation (They do not get all of their iron from mom during the 3 rd Trimester due to incomplete gestation) 10 5
Children at Risk for Iron Deficiency • Not receiving adequate iron in Diet • Drinking more than 24 oz. of milk/day • Rapid growth spurts where iron available cannot keep up with RBC production 11 Symptoms of Iron Deficiency • Pallor (paleness of the skin) • Tiredness, weakness or fatigue • CNS symptoms in severe anemia– Faintness–Dizziness–Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) –Headache–Spots before the eyes 12 6
Less O2 in Blood: Heart must work harder to pump enough oxygen to organs. Cardiac-related symptoms include: - Arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm) - SOB/shortness of breath - Chest pain 13 PICA • “Pica” - a craving to eat unusual substances such as ice or dirt (may also occur with high lead levels) • Numbness and tingling • Burning or sore tongue • Sores at the corner of the mouth • Chronic gastritis 14 7
Lead Toxicity Anemia increases the risk lead absorption more than normal, placing individuals at risk for lead toxicity 15 Iron Deficiency Anemia • Treatment begins with finding the underlying cause and correcting it. • Monitoring is best done by measuring the Hemoglobin concentration (Hgb). 16 8
Pernicious Anemia • Vitamin B-12 Deficiency (Cobalamin) • Megaloblastic Anemia (Large cells) • Caused by gastritis, parietal cell loss (cells in the stomach) & lack of IF (Intrinsic Factor) • Symptoms: anemia, fatigue, GI distress, neurological complications • Tx: B-12 injections, Oral suppl or diet 17 Sickle Cell Anemia • Sickling from mutation of the hemoglobin gene • Occludes small bv and causes tissue damage • RBC lifespan is shortened from 120 days to 20 days => Anemia 18 9
Sickle Cell Anemia • 10% American blacks & 25% of Africans are Heterozygotes (recessive/carrier) • Helps protect against malaria • 1970s: 20 year life expectancy • Today: 45 year life expectancy • Still required to check Hgb in WIC 19 Diagnosis A complete blood count test will check your levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin. 20 10
Red blood cells: • Average size • Variability in size • Volume • Hemoglobin concentration 21 Michigan WIC Low Hemoglobin 9/14 11/16 3/20 • PG Women 13.8% 17.5% 12.5% • BF Women 29.0% 33% 30.5% • NPP Women 36.5% 42% 41.0% • Children 12.4% 13.9% 10.4% • Infants 0.2% 0.3% 0.2% To Access Report: Clinic Module, Reports, Nutrition & Health Summary, Client Risk Factors by Category 22 11
2.16 Hematological Risk Determination Policy 23 Hematological Risk 200 Series • Iron Status • Lead Status 24 12
Low Iron Risk Category 201 • Criteria (PG, BE, BP, NPP, IBE, IBP, IFF, C1 – C4) • Low hematocrit (hct.)/ low hemoglobin (hgb.) cutoff value: At the time the blood test was taken, any value less than (<) the blood values listed in the following chart. • Note: Women who smoke, the blood value criterion based on: #of cigarettes smoked and trimester of pregnancy. (One pack of cigarettes = 20 cigarettes) 25 Cut-off values are available for reference from this button 26 13
When Do I Need To Do Bloodwork? Infants • One test between 7 and 13 months • At the ONE YEAR CERT visit if added to WIC BEFORE 7 MONTHS of age • If added to WIC AFTER 7 months, take the blood at the INITIAL certification visit 27 **Guidance for Infant Testing A hematological test prior to the 9-12 month recommended period may be appropriate when there are indications that the infant is at risk for low serum iron, as described below: • Low birth weight or preterm infant. • Has not been fed iron-fortified formula (10-12 mg. Fe/liter) or breastmilk. • Has a known diagnosis of anemia. • Has undergone surgery that resulted in excessive blood loss. 28 14
When Do I Need To Do Bloodwork? • Children Under • Two Before Two Two • 7-12 months • 13-24 months • Once between 13 and 24 months (prefer 6 mos. after first test) • For most C1’s, this will be at the 18 month CEVAL 29 When Do I Need To Do Bloodwork? Children Two - Five • Once after two years of age, THEN: • Once every 12 months if the previous result is above the cutoff level • Once every 6 months if the previous result is below the cutoff level 15
When Do I Need To Do Bloodwork? Pregnant Women • Once during pregnancy Postpartum Women • Once after delivery, preferably at least six weeks postpartum 31 Exemptions to Hematological Testing • Medical Condition Prohibits Draw • Religious Objections • Severe Risk to Staff • Pending (must have State approval) • Pandemic (Currently) 32 16
Add a row when no test is required/performed and select Exemption Reason Adding a row is NOT required for infants less than 7 months of age 33 Client Agreement Consent to WIC health screening : I will allow a WIC health screening for all WIC applicants in my family. WIC health screening includes answering health and diet questions, measuring height, weight and head size, and testing blood for iron level. 34 17
Referral Data • Must be within specified time period for the client’s status (6 month cut off) • Must be presented at the time of the appointment • The date of the test must be recorded in MI-WIC 35 Non-WIC Data enter the date blood work was done To enter Referral (Non-WIC) Data, use the date the test was performed, check the Non-WIC Data checkbox andnter Hgb value. 36 18
Retesting Local Agency Procedure • Testing levels that are outside the cutoff values in policy • A critical hemoglobin result <8 or >17 • Testing levels that have been specified as critical values established by local agency 37 Retest: explain reason 38 19
Follow-up Testing • One follow-up test is allowed when deemed necessary for health monitoring by CPA • Should be at least 60 days from previous test 39 MI-WIC: Lab Hx screen 40 20
41 21
Recommend
More recommend