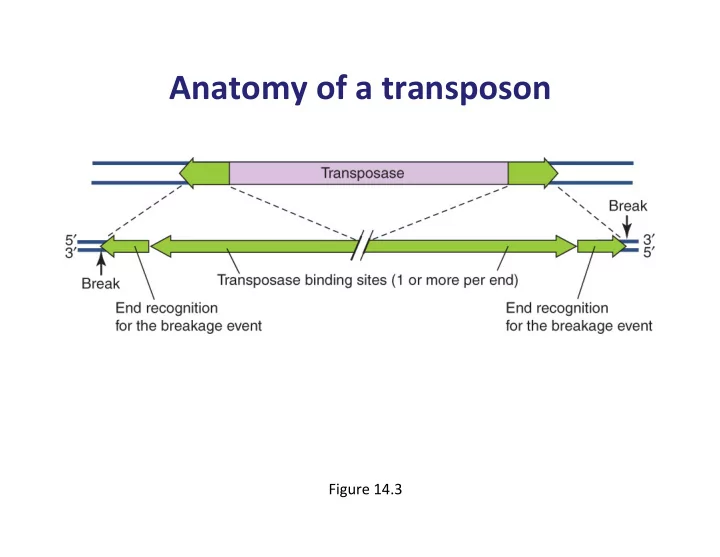

Anatomy ¡of ¡a ¡transposon ¡ ¡ Figure ¡14.3 ¡
Examples ¡of ¡some ¡bacterial ¡transposons ¡ Figure ¡14.10 ¡
Figure 10.27 IS 2 tnp Tn 5 IS 50 L IS 50 R tnp kan bleo str
Composite ¡transposons ¡have ¡ ¡ two ¡inser8on ¡elements ¡ Figure ¡14.11 ¡ Adapted ¡from ¡L. ¡Snyder ¡and ¡W. ¡Champness. ¡ Molecular ¡Gene,cs ¡of ¡Bacteria, ¡Second ¡ edi,on . ¡ASM ¡Press, ¡2003. ¡
The ¡transposase ¡binds ¡the ¡inverted ¡repeats ¡ Figure ¡14.4 ¡
Repair ¡of ¡gaps ¡flanking ¡the ¡new ¡inser8on ¡result ¡in ¡ target ¡site ¡duplica8on ¡ Figure ¡14.5 ¡
Figure 10.28 Target DNA sequence Transposable element Insertion Duplicated target sequence
Figure 10.29 Conservative transposition Replicative transposition Target sequence Tar DNA g e t st st DNA Ori Ori n n s s e p p c o u o s l s e Transposon Transposon excised from replicates donor D Tar get st N A mol Ori os n e s c p p u o s s n Donor DNA Transposon Donor DNA with break in new location undamaged
Replica8ve ¡transposons ¡leave ¡one ¡copy ¡of ¡the ¡ element ¡at ¡the ¡donor ¡site ¡ Figure ¡14.12 ¡
Cut-‑and-‑paste ¡transposi8on ¡results ¡in ¡excision ¡ and ¡integra8on ¡at ¡a ¡new ¡site ¡ Figure ¡14.8 ¡ Adapted ¡from ¡N. ¡C. ¡Craig, ¡et ¡al., ¡eds. ¡ Mobile ¡DNA ¡II . ¡ASM ¡Press, ¡2002. ¡
Regula8ng ¡transposi8on ¡with ¡DNA ¡ replica8on ¡can ¡increase ¡copy ¡number ¡of ¡cut-‑ and-‑paste ¡transposons ¡ Figure 14.9
Figure 10.30 Disrupted gene 2 Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 Gene 1 Gene A Gene 3 Gene A Transposon Chromosome Transposition Chromosome Transposition often results in a mutation since the newly moved Tn inactivates the gene where it has inserted.
Eukaryo8c ¡transposons ¡are ¡ ¡ similar ¡to ¡those ¡in ¡bacteria ¡ Figure ¡14.13 ¡ Adapted ¡from ¡F. ¡Bushman. ¡ Lateral ¡DNA ¡Transfer: ¡Mechanisms ¡and ¡ Consequences . ¡Cold ¡Spring ¡Harbor ¡Laboratory ¡Press, ¡2002. ¡
Recommend
More recommend