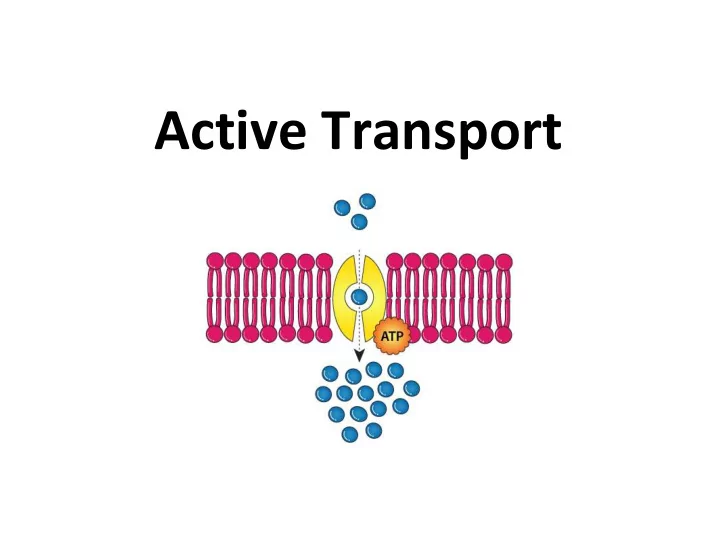

Active Transport
Active Transport Requires Energy • Why does active transport require energy? – Molecules are moving against the concentration gradient (low to high concentrations) OR – Process involves changes in membrane structure • The hydrolysis of ATP provides the energy to fuel active transport mechanisms
Passive Versus Active Transport
ATP Hydrolysis • ATP hydrolysis is the catabolic reaction process by which chemical energy that has been stored in the high-energy bonds in ATP is released by splitting these bonds
Active Transport – Membrane Pumps • Carrier proteins are used as pumps to move substances across the membrane from low to high concentration
Active Transport – Carrier Proteins • The sodium-potassium pump is an example of a carrier proteins that moves Na + ions and K + ions across the membrane against their gradients
Sodium-Potassium Pump • Found in many plasma membranes • Pumps out 3 Na + ions for every 2 K + ions taken in against the concentration gradient • Uses a tremendous amount of cellular energy (ATP)
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Why is the sodium-potassium (Na + /K + ) pump important? • Needed for proper muscle contraction and nerve cell impulse conduction • Prevents the build up of sodium (Na + ) within cells What would happen if too much sodium collected inside cells?
Active Transport – Bulk Transport • When molecules are too large to move through a channel protein or by using a carrier protein, vesicles are used to move the “bulk” material • Endocytosis (into the cell) – Phagocytosis (cell “eating”) – Pinocytosis (cell “drinking”) • Exocytosis (out of the cell)
Endocytosis • Transports substances into the cell • Cell membrane pinches around the materials, forms a vesicle and transports the materials into the cell
Example of Endocytosis: cholesterol uptake by cells
Endocytosis - Pinocytosis • Small amounts of extracellular fluid (and any dissolved solutes) are taken into the cell • Also known as “cell drinking”
Endocytosis - Phagocytosis • Solid materials are taken into cells • Also known as “cell eating”
Example of Phagocytosis • Phagocytes are specialized white blood cells that engulf and digest bacteria and dead or dying cells
Exocytosis • Transports bulk materials out of the cell • Vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and release the contents outside of the cell
Example of Exocytosis • An example of exocytosis is when neurons release neurotransmitters between cells to transmit nerve impulses
Endocytosis and Exocytosis Within the Same Cell
Active Transport Concept Map • Draw a summary concept map in your notes of active transport mechanisms
Cellular Transport Review Video
Recommend
More recommend