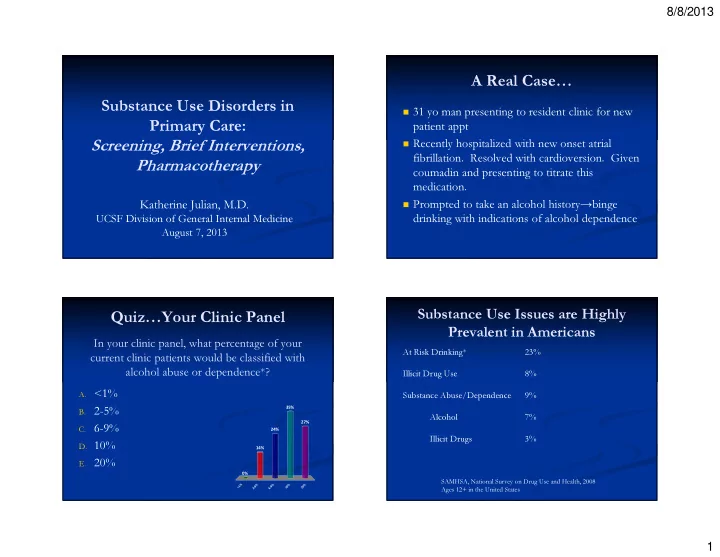

8/8/2013 A Real Case… Substance Use Disorders in � 31 yo man presenting to resident clinic for new Primary Care: patient appt � Recently hospitalized with new onset atrial Screening, Brief Interventions, fibrillation. Resolved with cardioversion. Given Pharmacotherapy coumadin and presenting to titrate this medication. � Prompted to take an alcohol history→binge Katherine Julian, M.D. drinking with indications of alcohol dependence UCSF Division of General Internal Medicine August 7, 2013 Substance Use Issues are Highly Quiz…Your Clinic Panel Prevalent in Americans In your clinic panel, what percentage of your At Risk Drinking* 23% current clinic patients would be classified with alcohol abuse or dependence*? Illicit Drug Use 8% A. <1% Substance Abuse/Dependence 9% 35% B. 2-5% Alcohol 7% 27% C. 6-9% 24% Illicit Drugs 3% D. 10% 14% E. 20% 0% SAMHSA, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2008 <1% 2-5% 6-9% 10% 20% Ages 12+ in the United States 1
8/8/2013 Alcohol Use Disorders in Older Alcohol Use in Primary Care Adults � 3% met full criteria for an alcohol use disorder � 3439 primary care patients � At-risk drinking was reported in: � 11% had “at risk” � 17% of men, 11% of women ages 50+ drinking defined as any � 19% of all respondents ages 50-64 of the following: � 13% of all respondents ages 65+ � > 2 drinks/day � Binge drinking was reported in: � > 2 episodes of 5+ � 20% of men, 6% of women ages 50+ drinks/day in 30 days � 23% of all respondents ages 50-64 � Drinking and driving � 15% of all respondents ages 65+ Curry SJ, et al. Prev Med 2000;31(5):595-607 NSDUH, 2009 Blazer D, Wu L. Am J Psychiatry, 2009 Outline Why SBIRT? The Evidence… � Substance Use Disorders - Definitions � Brief interventions can reduce alcohol use for at � SBIRT least 12 months in patients who are not alcohol � Screening : quickly assess use and severity of dependent. alcohol, illicit drugs, and prescription drug abuse � Brief Intervention : a 3-5 minute motivational � 10-30 % of patients can be expected to change intervention given to risky or problematic substance their drinking behaviors as a result of a brief users intervention. � Referral to Treatment � Motivational Interviewing � ETOH and Opiate Substance Use Pharmacotherapy Babor & Higgins-Biddle, 2000; Fleming and Manwell, 1999. 2
8/8/2013 Quiz… Definition – At Risk Drinking Which of the following is NOT considered � Men to be “at risk” drinking? • >4 drinks/day or A. 45 yo woman who drinks 1-2 • >14 drinks/week glasses of wine each night � Women (and > than 65 yrs) B. 70 yo man who drinks 1-2 beers 64% • >3 drinks/day or each night • >7 drinks/week C. 25 yo woman who drinks 4-5 � Increased risk of alcohol-related drinks once a week when she goes problems 17% 11% out with friends 8% D. 40 yo man who drinks 1-2 glasses . . . . . . . . . . . . h o h o w w of wine each night h h n w n w a n a n m m a a m m o o w w o o o y o y y y 0 0 5 7 5 4 4 2 Quiz… What is a Drink? A standard drink is any drink that contains about 14 grams of � Which of the following is NOT pure alcohol (about 0.6 fluid considered to be “at risk” drinking? ounces or 1.2 tablespoons) A. 45 yo woman who drinks 1-2 glasses of wine each night B. 70 yo man who drinks 1-2 beers each night C. 25 yo woman who drinks 4-5 drinks once a week when she goes out with friends D. 40 yo man who drinks 1-2 glasses of wine each night 3
8/8/2013 New DSM5 - Substance Use New DSM5 - Substance Use Disorder Disorder � “Maladaptive pattern of substance use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as � No longer need to differentiate between manifested by 2 (or more) of the following, occurring substance abuse and substance dependence within a 12-month period:” � Each substance can be categorized as a disorder � Failure to fulfill role obligations � Ex: Alcohol use disorder, stimulant use � Recurrent substance use in situations that are physically hazardous disorder, etc � Persistent use despite social/interpersonal problems � Grade Severity: Mild, Moderate, Severe Criteria for Substance Use Disorder Screening (contd) � Tolerance Some key opportunities include: � Withdrawal � As part of a routine examination � Using more than originally intended � Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut-down � Before prescribing a medication that interacts with � Time spent obtaining/using substance or recovering from side effects alcohol or other drugs � Reduction of social/occupational activities � In the emergency department or urgent care center � Use despite physical/psychological problems � Craving � When seeing patients who.. � Need 2 criteria for SUD � Are pregnant or trying to conceive � Have health problems that might be alcohol or drug induced/ � 2-3 criteria =mild related � 4-5 = moderate � Have a chronic illness not responding to treatment � >6 = severe � Are likely to drink heavily NIAAA, 2005. Helping Patients Who Drink Too Much: A Clinician’s Guide (Updated) 4
8/8/2013 How to Screen? How to Screen? � Ask permission: “Would it be ok to spend the next few � Single Drug Use Screen Question: minutes talking about alcohol?” � Pre-screen: Do you sometimes drink beer, wine, or � How many times in the past year have other alcoholic beverages? you used an illegal drug or used a � Single Alcohol Screen Question: prescription medication for � Men: How many times in the past year have you had 5 or nonmedical reasons? more drinks in one day? � Women (or >65 yo): How many times in the past year � Positive Screen=1 or more have you had 4 or more drinks in one day? � Positive Screen=1 or more Smith PC, et al. J Gen Intern Med 2009;24(7); Smith PC, et al. J Gen Intern Med 2009;24(7); NIAAA Guidelines 2005 NIAAA Guidelines 2005 A Positive Screen… Evidence for the Single Screen � Single Question Screen � Sensitivity/specificity: 88%/ 67% for alcohol use d/o � 1 or more heavy drinking days � Sensitivity/specificity: 82%/79% for unhealthy use � Any positive drug screen � CAGE: � What to do next? Assess… � Sensitivity/specificity: 92%/ 48% for alcohol dependence � Determine how many drinks/day in a week � Ask which drugs the patient has been using � AUDIT � Ask about negative impacts � Sensitivity/specificity: 96%/ 57% for unhealthy use � Sensitivity/specificity: 90%/ 61% for alcohol use d/o The follow-up questions are to assess impact and whether � Single Drug Screen or not use is serious enough to warrant a � Sensitivity/ specificity: 100%/ 74% for drug disorder substance use disorder diagnosis. � Sensitivity/specificity: 71%/ 95% for use with consequences Smith PC, JGIM 2009; Smith PC, Arch Intern Med 2010 5
8/8/2013 Criteria for Substance Use Determining “At Risk” vs. “Substance Use Disorder” Disorder � Failure to fulfill role obligations � Pts who meet criteria for “at-risk” should get a brief � Recurrent substance use in situations that are physically hazardous intervention � Persistent use despite social/interpersonal problems � Tolerance � Patients who meet substance use disorder criteria abuse should get a � Withdrawal � Using more than originally intended Brief intervention � AND � Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut-down A referral to specialty care (if they are willing) � Time spent obtaining/using substance or recovering from side � effects AND � Reduction of social/occupational activities Be considered for pharmacotherapy � � Use despite physical/psychological problems � Craving What is a Brief Intervention? Brief Intervention � Non-judgmental but give direct, honest feedback � Advise and Assist the patient � Provide advice on what a patient should do � Short, 3-5 minute motivational interviews that encourage patients to create a plan of action (ex: � Negotiate a concrete, realistic plan for behavioral change reduce drinking) that is based on their willingness to change their behavior � If not ready to change→harm reduction � Feedback and recommendations are given � Plan for follow-up respectfully in the form of useful information. 6
8/8/2013 HOW TO HELP PATIENTS: A CLINICAL APPROACH: NIAAA 2005 Resource for Clinicians HOW TO HELP PATIENTS: A CLINICAL APPROACH AT-RISK DRINKING AT-RISK DRINKING Advise and Assist Advise and Assist � State your conclusion and � State your conclusion and recommendation clearly recommendation clearly “You are drinking more “I strongly recommend than is medically safe.” that you cut down (or quit) and I’m willing to help.” image credit: Comstock image credit: Comstock HOW TO HELP PATIENTS: A CLINICAL APPROACH HOW TO HELP PATIENTS: A CLINICAL APPROACH AT-RISK DRINKING AT-RISK DRINKING Advise and Assist Advise and Assist Is the patient ready to commit to � State your conclusion and change at this time? recommendation clearly NO � Gauge readiness to change Do not be discouraged. drinking habits A mbivalence is common. Your advice has likely prompted a change in your patient’s “Are you willing to thinking. With continued reinforcement, your consider making changes patient may decide to take action. For now, restate your concern about his or in your drinking?” her health. image credit: Comstock 7
Recommend
More recommend