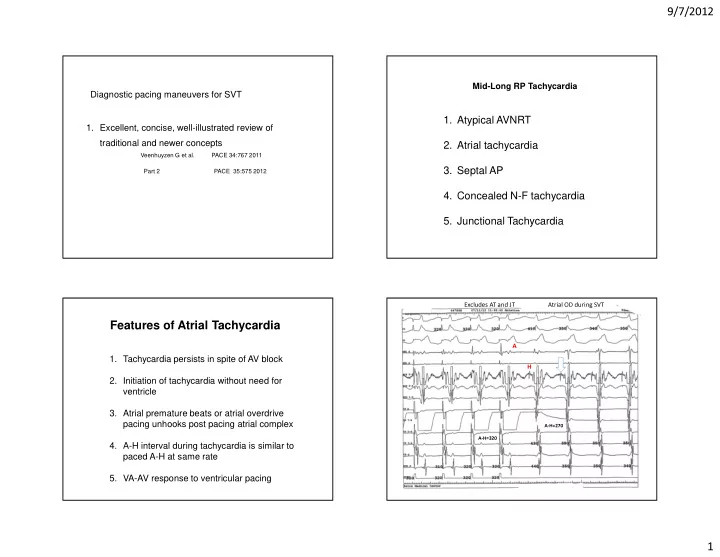

9/7/2012 Mid-Long RP Tachycardia Diagnostic pacing maneuvers for SVT 1. Atypical AVNRT 1. Excellent, concise, well-illustrated review of traditional and newer concepts 2. Atrial tachycardia Veenhuyzen G et al. PACE 34:767 2011 3. Septal AP Part 2 PACE 35:575 2012 4. Concealed N-F tachycardia 5. Junctional Tachycardia Excludes AT and JT Atrial OD during SVT Features of Atrial Tachycardia A 1. Tachycardia persists in spite of AV block H 2. Initiation of tachycardia without need for ventricle 3. Atrial premature beats or atrial overdrive pacing unhooks post pacing atrial complex A-H=270 A-H=320 4. A-H interval during tachycardia is similar to paced A-H at same rate 5. VA-AV response to ventricular pacing 1
9/7/2012 Atrial Tachycardia Pseudo V-A-A-V response VAAV response V-A-H response (HV>VA) 600ms VOP S-V >85, cPPI-TCL (PPI-TCL- ) >110ms favors AVNRT PACE 34:767 2
9/7/2012 Response to VOD during ORT Entrainment for distinguishing atypical AVNRT from Septal AP with long RP relationship 1. In all pts. With typical septal AP: PPI – TCL = <115ms and SA-VA = <85ms 2. 6/12 with slowly conducting AP: PPI – TCL >115ms and SA-VA = >85ms 3. Slowly conducting AP frequently give entrainment criteria similar to AVNRT a. SA - VA < 85 ms b. PPI - TCL < 115 ms Bennett M/Klein G. Circ Arrhythm 4:506, 2011 Michaud et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;38:1163-7 OTHER PITFALLS USING VOP DURING Manifest fusion best recognized when SVT pacing near the AP • Tachycardia may terminate • Doesn’t prove that pathway is part of circuit • Not appropriate for left lateral AP 3
9/7/2012 Manifest fusion during entrainment VOP during ORT unfused Capture with first fused Ventricular paced complex Entrained with fusion Ventricular complexes PACE 34:767 VOP during AVNRT Number of non fused V to capture A Capture by 4 th beat and and no fusion favors AVNRT Dandamuda Heart Rhythm 7 1326 4
9/7/2012 Novel approach to differentiating ORT from AVNRT PITFALLS USING VOP DURING SVT 1. In all orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia (ORT) 1. Doesn’t distinguish decremental AP patients atrial capture occurred after the first non- fused paced QRS in all patients during ventricular 2. Doesn’t distinguish presence of overdrive pacing (VOP) bystander AP 2. All AVNRT patients showed atrial capture after 2 or 3 beats after the first unfused QRS 3. Fusion with capture may not be seen 3. Technique most valuable for patients who have within 3 beats in left lateral AP SVT termination during VOP Limitations : may not distinguish AP bystander Dandamudi et al. Heart Rhythm 7:1326, 2010 Para-Hisian pacing demonstrating retrograde conduction over AV nodal pathway Insert PVC close to atrial insertion of AP PACE 35:757 2012 Hirao, K. et al. Circulation 1996;94:1027-1035 5
9/7/2012 Para-Hisian pacing demonstrating retrograde Determination of inadvertent atrial capture during para-hisian pacing conduction over Anteroseptal AP 1. Stim HRA and Stim PCS were measured during atrial capture 2. Stim HRA <70ms or stim PCS <60ms – was always observed with atrial capture 3. Stim HRA >100ms or stim PCS >90ms – observed only in absence of atrial capture 4. Stim HRA <85ms and stim CS <85ms – highly sensitive to detect atrial capture 5. For those in overlap zone � reposition catheter Obeyesekere/Klein G Circ Arrhythm 4:510, 2011 Hirao, K. et al. Circulation 1996;94:1027-1035 Inadvertent atrial capture during p- PITFALLS USING PARA-HISIAN hisian pacing 4:510.2011 ENTRAINMENT 1. Relative conduction times of retrograde nodal vs AP 2. Not reliable for left lateral AP 3. Proves presence of septal AP but doesn’t mean the AP is critical to circuit 4. Inadvertent Atrial capture 6
9/7/2012 Narrow complex tachycardia with VA Narrow complex tachycardia with VA block block AV nodal Junctional Concealed reentrant tachycardia nodofascicular PACE 35:757 2012 tachcyardia tachycardia Concealed nodofascicular tachycardia Concealed nodofascicular tachycardia • SVT initiated with atrial programmed stimulation (often with dual response) or ventricular extrastimuli • Evidence of AV dissociation during SVT or A on V TACH. SVT (rules out extranodal AP) • PVC on His during SVT advances the next His / V or terminates SVT • Bundle branch block leads to prolongation of VA interval or tachycardia cycle length 7
9/7/2012 Proposed circuit for left sided Proposed circuit for left sided Ablator signal within CS in sinus rhythm concealed nodofascicular tachycardia concealed nodofascicular tachycardia I aVF V 1 V 6 CS p CS d ABL RVA Focal Junctional Tachycardia Focal Junctional Tachycardia • Narrow complex tachycardia at times associated with AV dissociation often irregular • Catecholamine stimulation (abnormal automaticity) • Initiation with atrial and ventricular overdrive pacing (triggered) • Termination with adenosine (triggered) • Earliest retrograde A preceded or buried in the QRS • Late APD after His is committed does not affect tachycardia 8
9/7/2012 Early APD captures V A on His delays next A AVNRT JT terminate AVNRT JT PACE 35:757 2012 VOD in Left Lateral Accessory Pathway with capture after 3 rd unfused Conclusion QRS • Ventricular Pacing maneuvers are key to separating atypical AVNRT from Septal AP • Nodo-Fascicular/Ventricular diagnosed by excluding Atrial participation but finding evidence for an accessory pathway 300 msec • Junctional tachycardia best diagnosed at onset with out need for critical AH and response to late and early APCs 9
9/7/2012 Obeyeskere/Klein JCE 2011 SA-VA=75 cPPI-TCL= 110ms PACE 34 767 2011 The 2 nd paced beat (fused) terminates Successful ablation site in the CS SVT proves AVRT CS His His Ablator Ablator RV CS RV RAO view LAO view PACE 34:767 10
9/7/2012 Veenhuyzen PACE 34:767 2011 Excludes AT and JT PACE 35:757 2012 Long RP tachycardia ORT PACE 35:757 2012 11
9/7/2012 State Of The Art Advanced Heart Failure And Arrhythmia Management Integrating Devices And Pharmacotherapies October 27, 2012 The Stanford Court Hotel SF, CA Circ Arrhythm August 2011 12
Recommend
More recommend