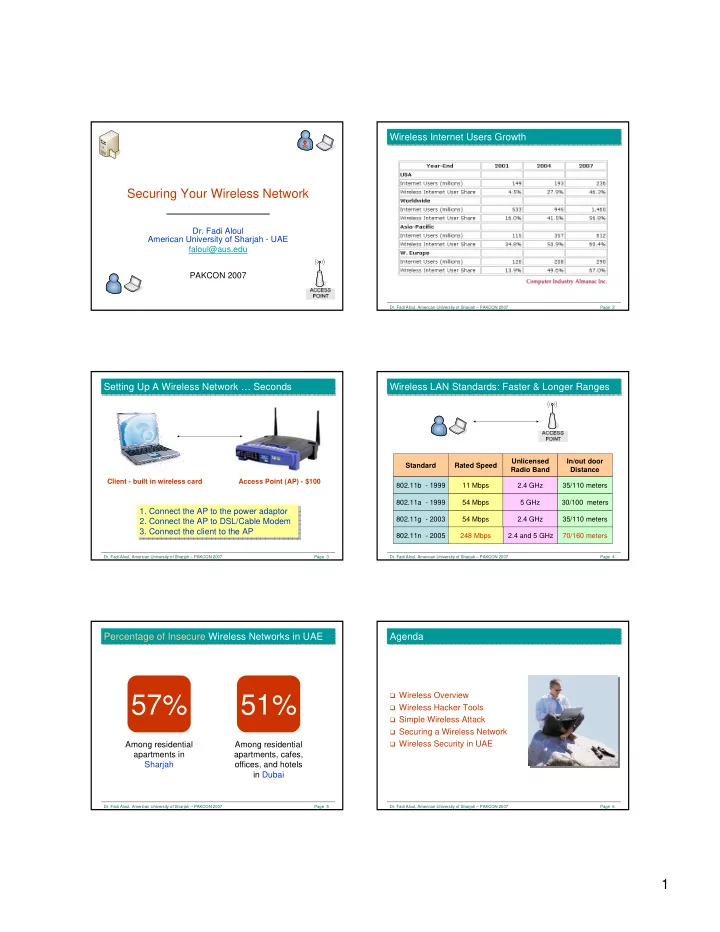

Wireless Internet Users Growth Wireless Internet Users Growth � Securing Your Wireless Network Dr. Fadi Aloul American University of Sharjah - UAE faloul@aus.edu PAKCON 2007 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 2 Setting Up A Wireless Network … Seconds Setting Up A Wireless Network … Seconds Wireless LAN Standards: Faster & Longer Ranges Wireless LAN Standards: Faster & Longer Ranges Unlicensed In/out door Standard Rated Speed Radio Band Distance Client - built in wireless card Access Point (AP) - $100 802.11b - 1999 11 Mbps 2.4 GHz 35/110 meters 802.11a - 1999 54 Mbps 5 GHz 30/100 meters 1. Connect the AP to the power adaptor 1. Connect the AP to the power adaptor 802.11g - 2003 54 Mbps 2.4 GHz 35/110 meters 2. Connect the AP to DSL/Cable Modem 2. Connect the AP to DSL/Cable Modem 3. Connect the client to the AP 3. Connect the client to the AP 802.11n - 2005 248 Mbps 2.4 and 5 GHz 70/160 meters Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 3 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 4 Percentage of Insecure Wireless Networks in UAE Agenda Percentage of Insecure Wireless Networks in UAE Agenda � Wireless Overview 57% 51% � Wireless Hacker Tools � Simple Wireless Attack � Securing a Wireless Network Among residential Among residential � Wireless Security in UAE apartments in apartments, cafes, Sharjah offices, and hotels in Dubai Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 5 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 6 1
Simple Wireless Network Simple Wireless Network Wireless Overview Service set identifier (SSID) - Unique 32-char identifier that wireless networking devices use to establish and maintain wireless connectivity - SSID sent in ‘beacon frames’ every few seconds (in plain text)! - Default SSID’s are well known (Linksys AP’s default to linksys, CISCO defaults to tsunami, etc) Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 7 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 8 Simple Wireless Network Simple Wireless Network Wireless Hacker Tools Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 9 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 10 Wireless Hacker Tools Wireless Hacker Tools Wireless Hacker Tools Wireless Hacker Tools � Hardware � Software � Omni directional high-gain antenna - $100 � Netstumbler, Kismet • General purpose surveying and war driving • Detect wireless networks � Directional high-gain antenna - $100 � Ethereal • Picks up weak signals many kilometers away • Sniff the network � Laptop - $500 � Airsnort • Crack WEP encryption keys Backtrack Backtrack Bootable Linux CD with many security Bootable Linux CD with many security auditing tools – Free! auditing tools – Free! http://www.remote-exploit.org/backtrack.html http://www.remote-exploit.org/backtrack.html Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 11 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 12 2
Simple Wireless Attack Simple Wireless Attack 1. Detect a wireless network 1. Detect a wireless network Simple Wireless Attack Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 13 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 14 War Driving War Driving War Driving War Driving � Wireless networks can be detected using: Sniff all 802.11 (wireless) traffic on the run Sniff all 802.11 (wireless) traffic on the run � � Beacon Sniffers monitor ‘beacon frames’ put out by APs � Will not hear from APs with disabled SSID broadcasting � Records: Signal Strength; MAC Address; SSID; Channel details � e.g. NetStumbler Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 15 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 16 War Driving Tool: NetStumbler War Driving Tool: NetStumbler � Wireless networks can be detected using: � � Passive Sniffers monitor exchanged packets between clients and AP and extract the SSID � Each packet has the AP SSID in plain text � e.g. Kismet and Airmagnet Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 17 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 18 3
Tool: Kismet War Chalking Tool: Kismet War Chalking Labeling a network to help other war drivers identify Labeling a network to help other war drivers identify the open wireless network the open wireless network Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 19 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 20 War Chalking War Chalking War Chalking War Chalking � Open Network � 802.11b Access Point � 2.0 Mb/s Bandwidth � SSID tsunami Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 21 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 22 Simple Wireless Attack Simple Wireless Attack Simple Wireless Attack Simple Wireless Attack 2. Use a Sniffer to log transmitted packets 3. Encrypted Network? - Break WEP Encryption Keys 2. Use a Sniffer to log transmitted packets 3. Encrypted Network? - Break WEP Encryption Keys Run AirSnort for a few hours. It will find the Encryption Key Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 23 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 24 4
Simple Wireless Attack Simple Wireless Attack 4. Access the internet for free ☺ 4. Access the internet for free ☺ Securing a Wireless Network Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 25 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 26 1) Change & Hide SSID Name 1) Change & Hide SSID Name 1) Change & Hide SSID Name 1) Change & Hide SSID Name � � Default SSID reveals AP brand name, change it! � No obvious SSID names, e.g. address or company name � Makes it difficult to detect the presence of an AP or its brand � Passive sniffers detect APs with disabled SSID broadcasting � Once detected, hackers can connect � If AP brand is detected, hacker can run exploits or use default password Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 27 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 28 2) Change Default AP Administrator Password 2) Change Default AP Administrator Password 2) Change Default AP Administrator Password 2) Change Default AP Administrator Password � Websites list default AP administrative passwords � If hacker connects to AP configuration page, he/she owns the AP! Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 29 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 30 5
3) MAC Filtering 3) MAC Filtering 3) MAC Filtering 3) MAC Filtering � � Restrict users with allowed MAC addresses to connect to the AP � Allow access by wireless cards with authorized MAC addresses only � Hard to manage in large organizations � MAC addresses are transmitted in clear text � Easy to capture � Easy to spoof MAC address on hacker machine (e.g. SMAC) Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 31 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 32 4) Control Your AP Broadcast Area 4) Control Your AP Broadcast Area 5) Enable Encryption 5) Enable Encryption � Encrypted No signal ???? � Adjust signal strength and direction � � Place AP far away from exterior walls and windows � Add window coverings or wall paintings to reduce the wireless signal � WEP encrypts messages exchanged between client and AP � Use directional antenna � WEP uses 40-bit RC4 encryption key � WEP key shared among all users � Antenna placement and signal suppression doesn’t encrypt data � Each packet includes a 24-bit initialization vector (IV) – � Hackers use advanced antennas that pick up a weak signal from (i.e. 16,777,216 possible IV’s) several kilometers away � WEP combines the IV with the 40-bit key to encrypt data � Lowering the signal hurts legitimate users a lot more than it hurts the � WEP keys can be cracked after collecting enough packets (Airsnort) hackers � IV is the weakness; Increasing WEP key length is useless Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 33 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 34 5) Enable Encryption 5) Enable Encryption 5) Enable Encryption 5) Enable Encryption Encrypted ???? � � WPA encrypts messages exchanged between client and AP � WPA can be configured to use a pre-shared key among all users � WPA uses 128-bit RC4 key and 48-bit IV � WPA uses TKIP which dynamically changes keys during a session � WPA2 uses AES encryption – Solid algorithm � WPA pre-shared keys can be cracked if they are simple � WPA2 not supported by all wireless network cards or APs Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 35 Dr. Fadi Aloul, American University of Sharjah – PAKCON 2007 Page 36 6
Recommend
More recommend