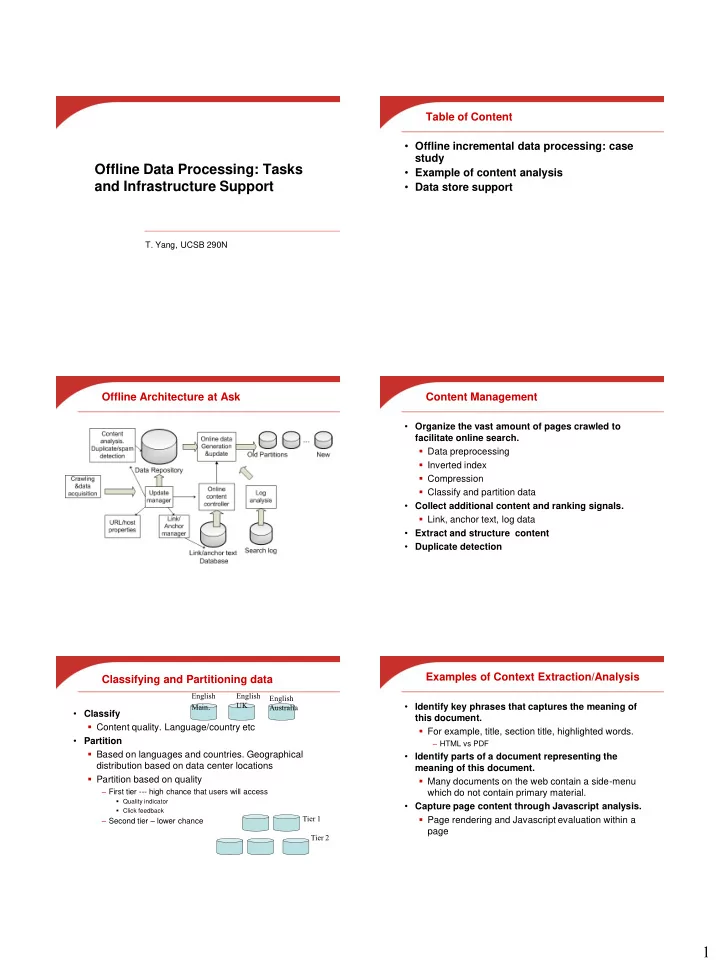

Table of Content • Offline incremental data processing: case study Offline Data Processing: Tasks • Example of content analysis and Infrastructure Support • Data store support T. Yang, UCSB 290N Offline Architecture at Ask Content Management • Organize the vast amount of pages crawled to facilitate online search. Data preprocessing Inverted index Compression Classify and partition data • Collect additional content and ranking signals. Link, anchor text, log data • Extract and structure content • Duplicate detection Examples of Context Extraction/Analysis Classifying and Partitioning data English English English Main . UK • Identify key phrases that captures the meaning of Australia • Classify this document. Content quality. Language/country etc For example, title, section title, highlighted words. • Partition – HTML vs PDF Based on languages and countries. Geographical • Identify parts of a document representing the distribution based on data center locations meaning of this document. Partition based on quality Many documents on the web contain a side-menu – First tier --- high chance that users will access which do not contain primary material. Quality indicator • Capture page content through Javascript analysis. Click feedback Tier 1 Page rendering and Javascript evaluation within a – Second tier – lower chance page Tier 2 1
Redundant Content Removal in Search Engines • Over 1/3 of Web pages crawled are near Example of Content Analysis duplicates • When to remove near duplicates? • Detect content block related Offline removal to the main content of a page Offline data Web Duplicate Non-content text/link Online processing Pages filtering index material is ignored or reduced Online removal with query-based duplicate in importance during removal indexing process Final results Online index Duplicate matching & User removal result ranking query Why there are so many duplicates? Tradeoff of online vs. offline removal • Same content, different URLs, often with different Online-dominating Offline-dominating approach approach session IDs. • Crawling time Impact to offline High precision High precision Low recall High recall difference Remove fewer Remove most of duplicates duplicates Higher offline burden Impact to online More burden to Less burden to online deduplication online deduplication Impact to overall Higher serving cost Lower serving cost cost Software Infrastructure Support at Ask Requirements for Data Repository Support in Offline Systems • Programming support (multi-threading/exception • Update Handling, Hadoop MapReduce) handling large volumes of modified documents • Data stores for managing billions of objects adding new content Distributed hash tables, queues etc • Random access • Hadoop Communication and data exchange among request the content of a document based on its URL machines/services • Execution environment • Compression and large files Controllable (stop, pause, restart). reducing storage requirements and efficient access Service registration and invocation • Scan service monitoring Scan documents for text mining. Logging and test framework. 2
Options for Data Stores • Bigtable at Google • Dynamo at Amazon • Open source software Technology Language Users/ Platform sponsors Apache Bigtable Java/Hadoop Apache Cassandra Dynamo Hypertable Bigtable C++/Hadoop Baidu Hbase Bigtable Java/Hadoop Apache LevelDB Bigtable C++ Google MongoDB C++ 3
Recommend
More recommend