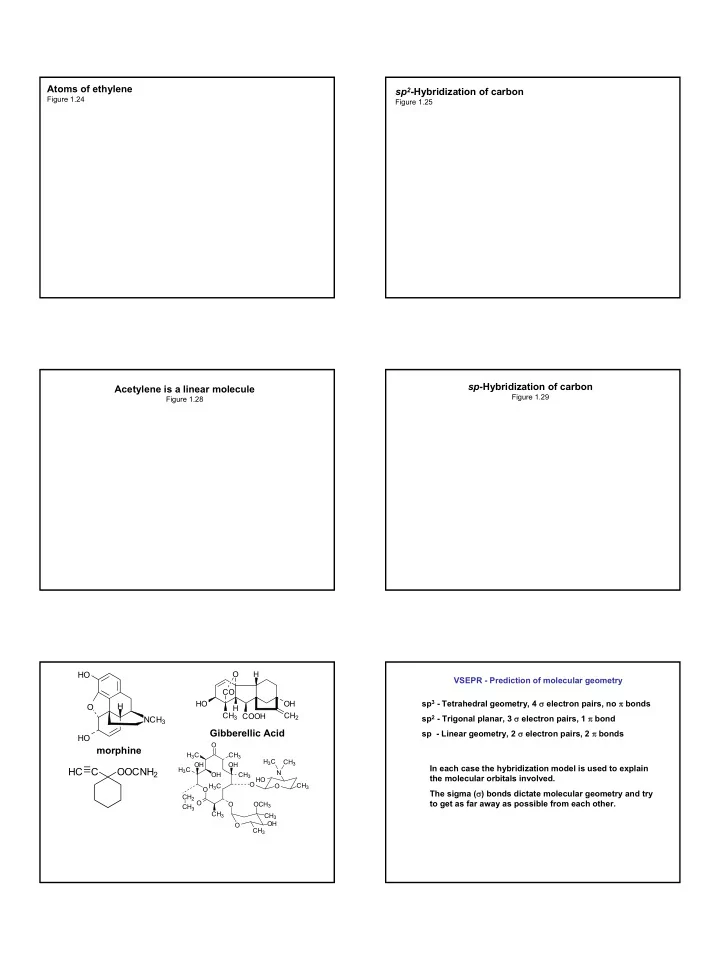

Atoms of ethylene sp 2 -Hybridization of carbon Figure 1.24 Figure 1.25 sp -Hybridization of carbon Acetylene is a linear molecule Figure 1.29 Figure 1.28 HO O H VSEPR - Prediction of molecular geometry CO sp 3 - Tetrahedral geometry, 4 σ electron pairs, no π bonds HO OH O H H CH 3 COOH CH 2 sp 2 - Trigonal planar, 3 σ electron pairs, 1 π bond NCH 3 Gibberellic Acid sp - Linear geometry, 2 σ electron pairs, 2 π bonds HO O morphine H 3 C CH 3 H 3 C CH 3 OH OH In each case the hybridization model is used to explain HC C OOCNH 2 H 3 C N OH CH 3 the molecular orbitals involved. HO O H 3 C O CH 3 O The sigma ( σ ) bonds dictate molecular geometry and try CH 2 CH 3 O to get as far away as possible from each other. O OCH 3 CH 3 CH 3 OH O CH 3 1
Functional group classifications Chapter 2 - Alkanes Classification of hydrocarbons: aliphatic or aromatic Aliphatic (“fat”) Aromatic (“smell”) Alkanes, alkenes, Arenes - benzenes, alkynes polyaromatics Classifications are old but still useful for organizing families of compounds Simple Alkanes Structural Isomers C 4 H 10 n -butane C 4 H 10 isobutane Methane (CH 4 ) Ethane (C 2 H 6 ) Propane (C 3 H 6 ) C 5 H 12 C 5 H 12 C 5 H 12 n -pentane isopentane Neopentane Careful with drawing chains! CH 3 CHCH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CHCH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CHCH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CHCH 3 CH 3 Table 2.2 – need to know names up to C12 All the same compound 2
IUPAC Rules and how to apply them Rules: Hexane (IUPAC); n -hexane (common) • Find the longest continuous carbon chain • Identify substituent groups attached to the chain Longest chain - hexane • Number the chain so as to keep numbers small substituent - methyl • Write the name in the following format: position on chain - 2 2-methylhexane not 5-methylhexane Numerical location - [substituent(s)][parent alkane] 3,4-dimethylheptane e.g. 2,3-dimethylheptane Alkyl Substituents Replace -ane ending with -yl H C C C C C C C C H H C Primary (1 o ) Secondary (2 o ) Tetriary (3 o ) CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 - H 3 C C CH 3 CH CH 3 Propyl group isopropyl group t-Butyl group 1-methylethyl 1,1-dimethylethyl 3
Recommend
More recommend