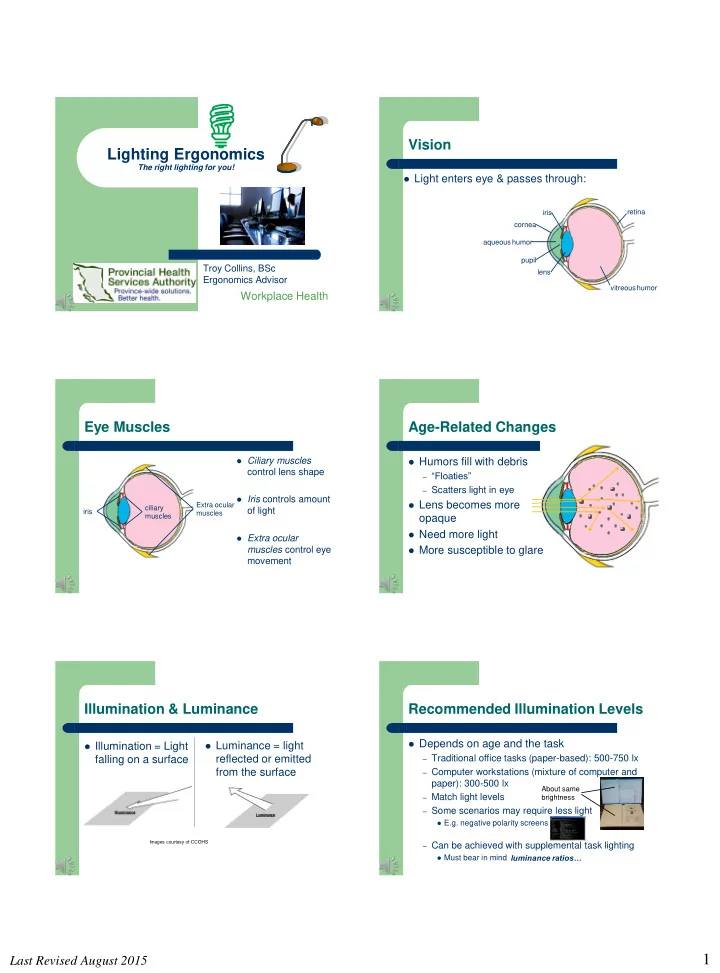

Vision Lighting Ergonomics The right lighting for you! Light enters eye & passes through: iris retina cornea aqueous humor pupil Troy Collins, BSc lens Ergonomics Advisor vitreous humor Workplace Health Eye Muscles Age-Related Changes Ciliary muscles Humors fill with debris control lens shape – “Floaties” – Scatters light in eye Iris controls amount Lens becomes more Extra ocular ciliary of light iris muscles muscles opaque Need more light Extra ocular muscles control eye More susceptible to glare movement Illumination & Luminance Recommended Illumination Levels Depends on age and the task Luminance = light Illumination = Light falling on a surface reflected or emitted – Traditional office tasks (paper-based): 500-750 lx from the surface – Computer workstations (mixture of computer and paper): 300-500 lx About same – Match light levels brightness – Some scenarios may require less light E.g. negative polarity screens Images courtesy of CCOHS – Can be achieved with supplemental task lighting luminance ratios… Must bear in mind 1 Last Revised August 2015
Luminance Ratios Luminance Ratios Ratio of amount of light Want balance of light coming from main task High luminance ratios cause pupils High luminance Low luminance area to secondary and to dilate and constrict continuously Moderate luminance other areas, for – Eye fatigue, discomfort, headaches example: Can also wash out details – Computer screen : paper – Too much light documents – Dispersion of light in eyes – Computer screen : window behind Glare Glare Sources: Direct Discomfort glare -causes discomfort only Direct-shining directly into the eye Disability glare -causes reduction in visual – Windows performance – Bright light fixture – Poorly adjusted task Blinding glare -makes it difficult to see lamp – E.g. bright headlights Image adapted from CCOHS Glare Sources: Indirect Glare Control Indirect Avoid direct view of light bulbs in design – Reflected from a Adjust task lighting not to shine into eyes or onto surface screen Desk Wall Floor Computer screen Power on Power off Image courtesy of CCOHS 2 Last Revised August 2015
Glare Control Glare Control Matte finishes Avoid task light being too bright Partitions Window blinds Create balanced brightness Windows to side Personal Control Glare Control Adjust the monitor contrast and Dual monitors: same Peaked or brimmed brightness to comfortable levels screen brightness hat Eliminate / control glare – Preferably white screen – Minimize upward screen tilt with black characters – Screen perpendicular to window Not as good for detail, Practice the 20/20/20 Rule : though – every 20 minutes – stare at an object 20 feet away – for 20 seconds Get your eyes checked at least every 2 years For More Information Visit our Ergonomics Page on the POD http://pod/empwell/ohsc/injprev/pages/Default.aspx 3 Last Revised August 2015
Recommend
More recommend