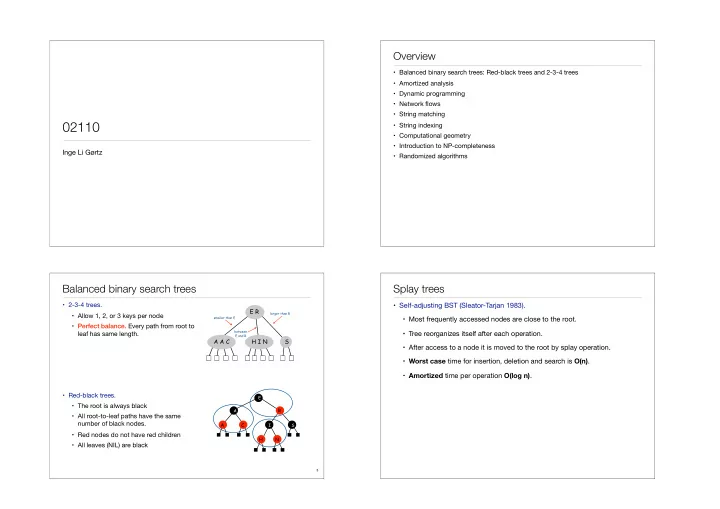

Overview • Balanced binary search trees: Red-black trees and 2-3-4 trees • Amortized analysis • Dynamic programming • Network flows • String matching 02110 • String indexing • Computational geometry • Introduction to NP-completeness Inge Li Gørtz • Randomized algorithms Balanced binary search trees Splay trees • 2-3-4 trees. • Self-adjusting BST (Sleator-Tarjan 1983). E R larger than R • Allow 1, 2, or 3 keys per node smaller than E • Most frequently accessed nodes are close to the root. • Perfect balance. Every path from root to between leaf has same length. • Tree reorganizes itself after each operation. E and R A A C H I N S • After access to a node it is moved to the root by splay operation. • Worst case time for insertion, deletion and search is O(n) . • Amortized time per operation O(log n) . • Red-black trees. E • The root is always black R A • All root-to-leaf paths have the same number of black nodes. A C I S • Red nodes do not have red children H N • All leaves (NIL) are black � 3
Splaying Splaying • Splay(x): do following rotations until x is the root. Let y be the parent of x. • Splay(x): do following rotations until x is the root. Let p(x) be the parent of x. • right (or left): if x has no grandparent. • right (or left): if x has no grandparent. • zig-zag (or zag-zig): if one of x,p(x) is a left child and the other is a right child. z z x y x w x w z right y x d d x w a c left a c a b c d a b b c b c a b right rotation at x (and left rotation at y) zig-zag at x Splaying Dynamic set implementations Worst case running times (except splay trees) • Splay(x): do following rotations until x is the root. Let y be the parent of x. • right (or left): if x has no grandparent. Implementation search insert delete minimum maximum successor predecessor • zig-zag (or zag-zig): if one of x,y is a left child and the other is a right child. linked lists O(n) O(1) O(1) O(n) O(n) O(n) O(n) • roller-coaster: if x and p(x) are either both left children or both right ordered array O(log n) O(n) O(n) O(1) O(1) O(log n) O(log n) children. BST O(h) O(h) O(h) O(h) O(h) O(h) O(h) 2-3-4 tree O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) z y x y x z y red-black tree O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) O(log n) d a x z splay tree O(log n) † O(log n) † O(log n) † O(log n) † O(log n) † O(log n) † O(log n) † a b c d c b †: amortized running time a b c d right roller-coaster at x (and left roller-coaster at z) � 8
↖ ↑ ↖ ↖ ↖ ← ↑ ↖ ↑ ↖ ← ↑ ↖ ↖ ↖ ↖ ↖ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↖ ↑ ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ↑ ↖ ↖ ↖ ↖ ↖ ← ← ← ↑ Dynamic Programming Amortized analysis • General algorithmic technique • Can be used when the problem have “optimal substructure”: solution can be constructed from optimal solutions to subproblems. • Amortized analysis. • Time required to perform a sequence of data operations is averaged over all the operations performed. • Example: dynamic tables with doubling and halving • Examples • If the table is full copy the elements to a new array of double size. • Weighted interval scheduling • If the table is a quarter full copy the elements to a new array of half the size. • Segmented least squares • Worst case time for insertion or deletion: O(n) • Sequence alignment • Amortized time for insertion and deletion: O(1) • Shortest paths (Bellman-Ford) • Any sequence of n insertions and deletions takes time O(n). • Methods. • Aggregate method • Accounting method • Potential method Sequence alignment Sequence alignment: Finding the solution Penalty matrix j δ if i = 0 A C G T j δ if i = 0 i δ if j = 0 if j = 0 A 0 1 2 2 i δ SA ( X i , Y j ) = α ( x i , y j ) + SA ( X i − 1 , Y j − 1 ) , SA ( X i , Y j ) = α ( x i , y j ) + SA ( X i − 1 , Y j − 1 ) , C 1 0 2 3 δ = 1 min δ + SA ( X i , Y j − 1 ) , otherwise δ + SA ( X i − 1 , Y j ) } min otherwise G 2 2 0 1 δ + SA ( X i , Y j − 1 ) , δ + SA ( X i − 1 , Y j ) } T 2 3 1 0 Penalty matrix A C A A G T C A C A A G T C A C A A G T C A C G T 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 C C 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 C ↑ A 0 1 2 2 δ = 1 A A 2 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 A ↑ C 1 0 2 3 T T 3 2 3 2 3 3 3 4 T SA ( X 5 , Y 3 ) G 2 2 0 1 Depends on ? G G 4 3 4 3 4 3 4 5 G T 2 3 1 0 T T 5 4 5 4 5 4 3 4 T � 11 � 12
Bellman-Ford Example OPT ( i , v ) = { 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Bellmann-Ford(G,s,t) if i = 0 0 s ∞ for each node v ∈ V otherwise a ∞ min{ OPT ( i − 1, v ), min ( v , w ) ∈ E { OPT ( i − 1, w ) + c vw }} M[0,v] = ∞ b ∞ M[0,t] = 0. c ∞ for i=1 to n-1 d ∞ for each node v ∈ V e ∞ M[i,v] = M[i-1,v] for each edge (v,w) ∈ E f ∞ Bellmann-Ford(G,s,t) M[i,v] = min(M[i,v], M[i-1,w] + c vw t 0 for each node v ∈ V ∞ M[0,v] = ∞ ∞ a 10 f M[0,t] = 0. 18 ∞ 9 for i=1 to n-1 b for each node v ∈ V 6 -16 6 19 M[i,v] = M[i-1,v] ∞ s 30 ∞ for each edge (v,w) ∈ E e -8 11 M[i,v] = min(M[i,v], M[i-1,w] + c vw d 15 6 20 16 ∞ 44 t 0 c ∞ � 13 � 14 Example Example 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Bellmann-Ford(G,s,t) Bellmann-Ford(G,s,t) s ∞ ∞ s ∞ ∞ 59 for each node v ∈ V for each node v ∈ V a ∞ ∞ a ∞ ∞ 29 M[0,v] = ∞ M[0,v] = ∞ b ∞ ∞ b ∞ ∞ 36 M[0,t] = 0. c ∞ 44 M[0,t] = 0. c ∞ 44 44 for i=1 to n-1 for i=1 to n-1 d ∞ 16 d ∞ 16 16 for each node v ∈ V for each node v ∈ V e ∞ 6 e ∞ 6 6 M[i,v] = M[i-1,v] M[i,v] = M[i-1,v] for each edge (v,w) ∈ E for each edge (v,w) ∈ E f ∞ 19 f ∞ 19 0 M[i,v] = min(M[i,v], M[i-1,w] + c vw M[i,v] = min(M[i,v], M[i-1,w] + c vw ) t 0 0 t 0 0 0 29 ∞ 19 0 a 10 a 10 f f 18 18 36 ∞ 9 9 b b 6 -16 6 6 -16 6 19 19 59 ∞ s 30 s 30 6 e e -8 11 -8 11 d d 15 6 15 6 20 20 16 16 16 44 44 t t 0 c c 44 � 15 � 16
Network Flow Network flow: s-t Cuts 1 • Network flow: 2 • graph G=(V,E). 2 2 • Cut: Partition of vertices into S and T, such that s ∈ S and t ∈ T. s 1 t • Special vertices s (source) and t (sink). 2 2 S T 2 • Every edge (u,v) has a capacity c(u,v) ≥ 0. t s • Flow: 1 • capacity constraint: every edge e has a flow 0 ≤ f(u,v) ≤ c(u,v). • flow conservation: for all u ≠ s, t: flow into u equals flow out of u. X X f ( v, u ) = f ( u, v ) • Capacity of cut: total capacity of edges going from S to T. u v :( v,u ) ∈ E v :( u,v ) ∈ E • Flow across cut: flow from S to T minus flow from T to S. • Value of flow f is the sum of flows out of s minus sum of flows into s: • Value of flow any flow |f| ≤ c(S,T) for any s-t cut (S,T). X X | f | = f ( s, v ) − f ( v, s ) • Suppose we have found flow f and cut (S,T) such that |f| = c(S,T). Then f is a v :( s,v ) ∈ E v :( v,s ) ∈ E maximum flow and (S,T) is a minimum cut. • Maximum flow problem: find s-t flow of maximum value Augmenting paths Scaling algorithm • Augmenting path (definition di ff erent than in CLRS): s-t path where • Scaling parameter Δ • forward edges have leftover capacity • Only consider edges with capacity at least Δ in residual graph G f ( Δ ). • backwards edges have positive flow • Example: Δ = 4 - δ + δ + δ + δ - δ - δ 1 1 s t G f f 1 < c 1 f 2 > 0 f 3 < c 3 f 4 < c 4 f 5 > 0 f 6 > 0 3 3 1 • There is no augmenting path <=> f is a maximum flow. 3 4 3 1 4 3 t • Ford-Fulkerson algorithm: s 5 6 • Repeatedly find augmenting path, use it, until no augmenting path exists 2 4 2 4 2 4 • Running time: O(|f*| m). 1 1 4 • Edmonds-Karp algorithm: 3 3 • Repeatedly find shortest augmenting path, use it, until no augmenting path exists 1 3 4 3 • Use BFS to find a shortest augmenting path. 1 4 3 • Running time: O(nm 2 ) G f (4) t s 5 6 • Find minimum cut. All vertices to which there is an augmenting path from s goes into 2 4 2 4 S, rest into T. 2 4 � 20 4
Network flow String Matching • Can model and solve many problems via maximum flow. • String matching problem: • Maximum bipartite matching • string T (text) and string P (pattern) over an alphabet Σ . |T| = n, |P| = m. • k edge-disjoint paths • Report all starting positions of occurrences of P in T. • capacities on vertices • String matching automaton. Running time: O(n + m| Σ |) • Many sources/sinks • lower bounds on flow on edges. • Knuth-Morris-Pratt (KMP). Running time: O(m + n) • assignment problems: Example. X doctors, Y holidays, each doctor should work at at most c holidays, each doctor is available at some of the holidays. 1 1 c c s t c Finite Automaton Finite Automaton • Finite automaton: alphabet Σ = {a,b,c}. P= ababaca. • Finite automaton: alphabet Σ = {a,b,c}. P= ababaca. a a accepting state accepting state starting state starting state a a a a a b a b a c a a b a b a c a b b a a b b longest prefix of P that is a suffix of ‘abaa'
Recommend
More recommend